Helper Scripts
Overview
AWS CloudFormation provides you with some helper scripts that you can use to install softwares or start services on EC2 instances created as part of your stack.
Here are the helper script AWS CloudFormation currently provides:
- cfn-init: use to retrieve and interpret metadata, install softwares, create files or start services.
- cfn-signal: use to signal that your resource is ready.
- cfn-hup: use to check for updates to metadata and execute custom hooks when changes are detected.
- cfn-get-metadata: use to retrieve the metadata for a resource.
To install the latest version of CloudFormation Helper Scripts, execute the command yum install -y aws-cfn-bootstrap on your EC2 instance.
Hands-on lab
This lab will guide you through some steps required to provision an EC2 instance with the package httpd being installed initially. You will utilize cfn-init, cfn-hup and cfn-signal to fulfill all tasks in this lab.
Configure cfn-init
In order to install packages, we need to provide the metadata AWS::CloudFormation::Init to our EC2 instance. Here, we specify the packages we want to install, files we want to create and services we want to start.
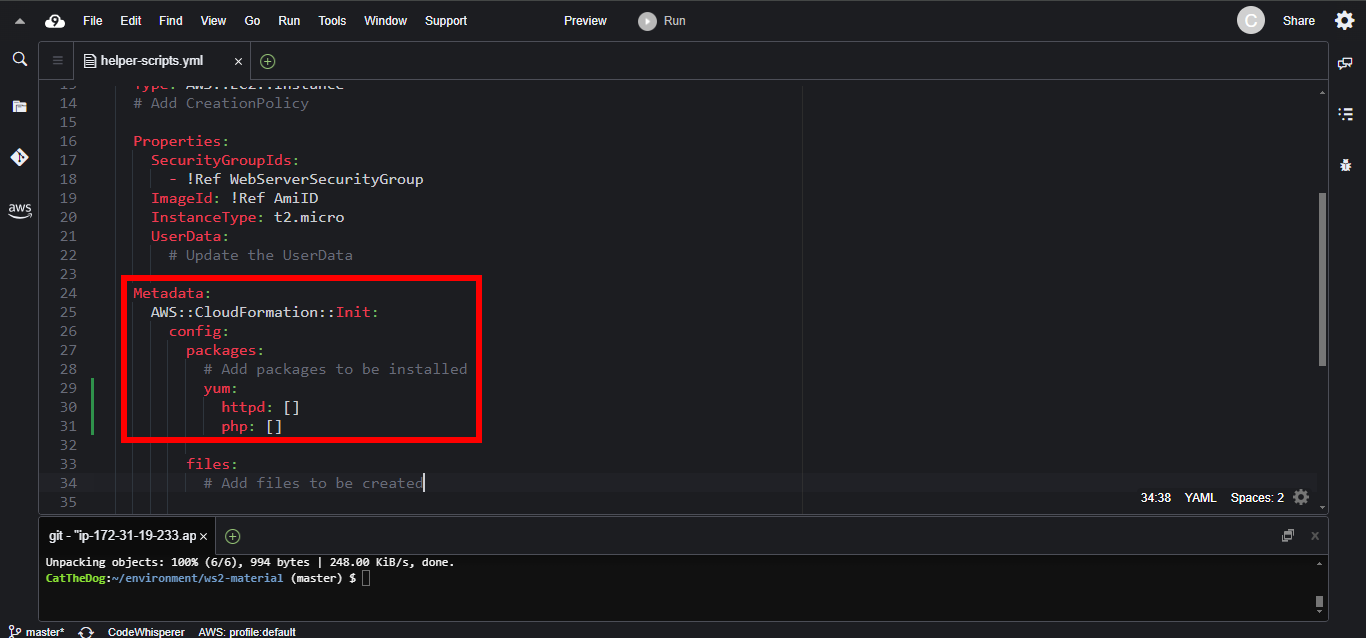
1. To be able to run a public PHP website, we need two packages, php and httpd. Let’s add them to the packages section.
Metadata:
AWS::CloudFormation::Init:
config:
packages:
yum:
httpd: []
php: []
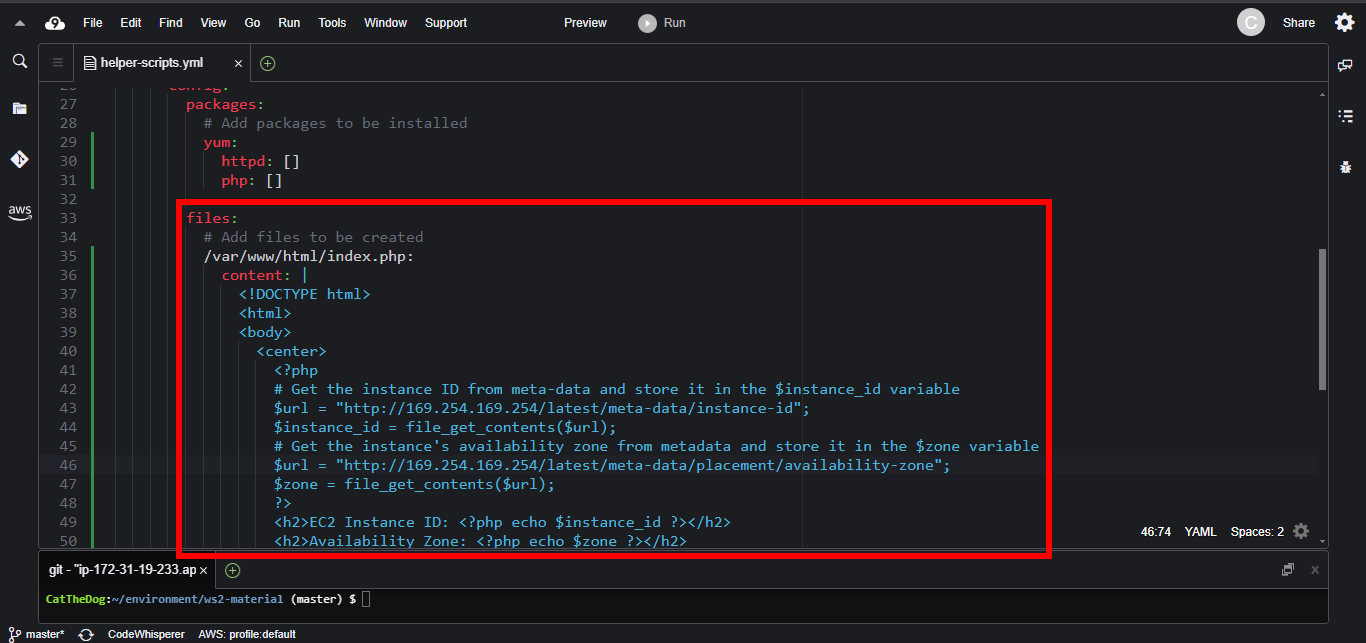
2. The httpd website needs a file serving as a home page, so we need to create one.
Add the index.php file to the files section. The first three zero digits 000 indicates that is not a symlink; the next three digits 644 indicates the permission of this file. We also specify that the owner and the group of this file is apache.
files:
# Add files to be created
/var/www/html/index.php:
content: |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<center>
<?php
# Get the instance ID from meta-data and store it in the $instance_id variable
$url = "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id";
$instance_id = file_get_contents($url);
# Get the instance's availability zone from metadata and store it in the $zone variable
$url = "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone";
$zone = file_get_contents($url);
?>
<h2>EC2 Instance ID: <?php echo $instance_id ?></h2>
<h2>Availability Zone: <?php echo $zone ?></h2>
</center>
</body>
</html>
mode: 000644
owner: apache
group: apache
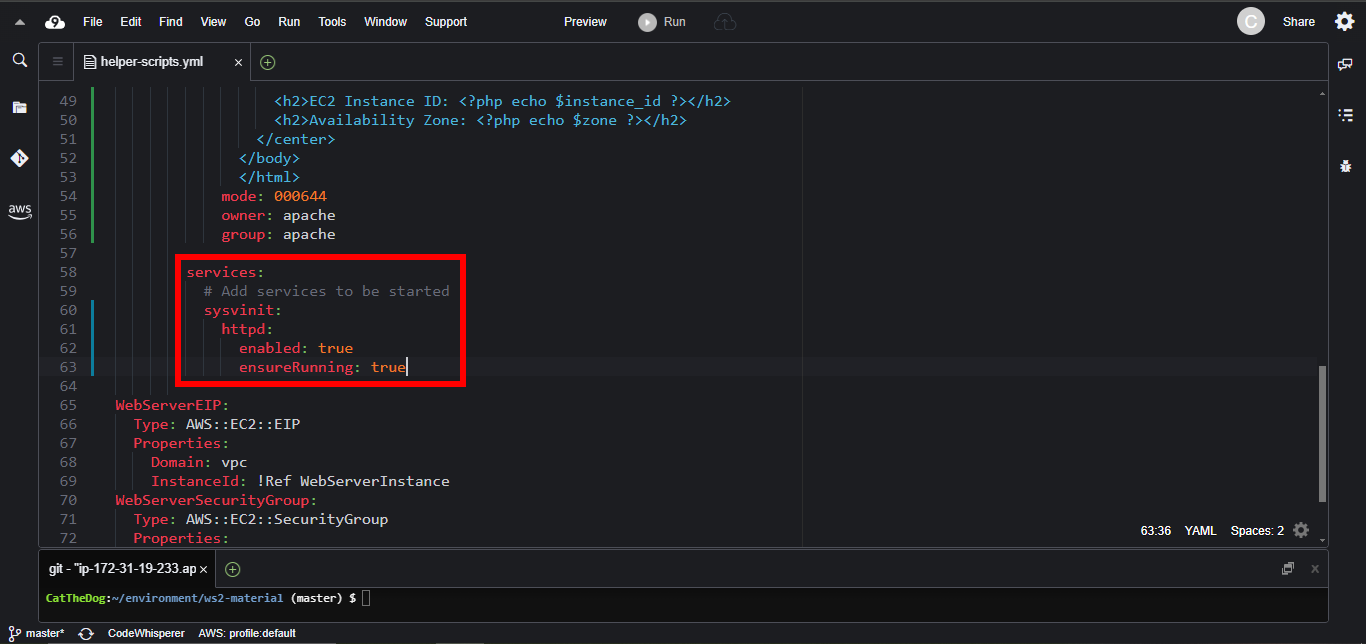
3. Enable the httpd so that it will automatically start on restart. On linux systems, the key which helps us defining that stuff is sysvinit.
services:
sysvinit:
httpd:
enabled: true
ensureRunning: true
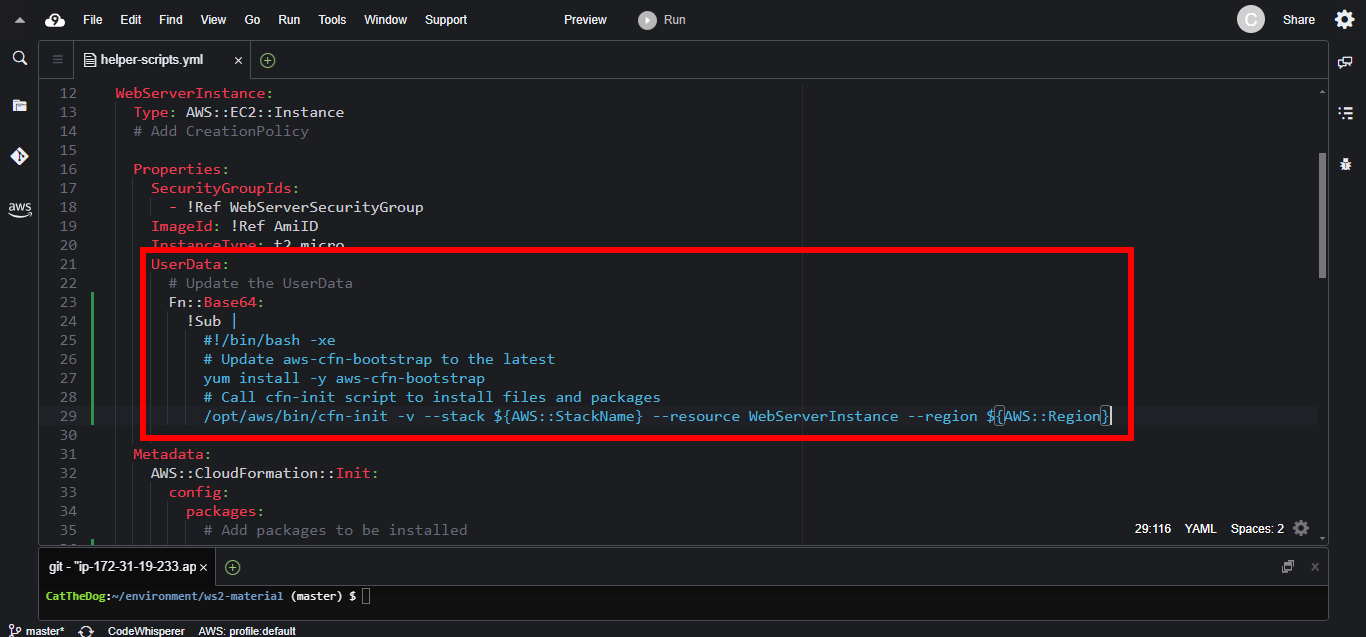
4. Call the cfn-init scripts in the UserData, where we can specify the commands for EC2 instance to execute when initializing stack.
Properties:
ImageId: !Ref AmiID
InstanceType: t2.micro
UserData:
# Update the UserData
Fn::Base64:
!Sub |
#!/bin/bash -xe
# Update aws-cfn-bootstrap to the latest
yum install -y aws-cfn-bootstrap
# Call cfn-init script to install files and packages
/opt/aws/bin/cfn-init -v --stack ${AWS::StackName} --resource WebServerInstance --region ${AWS::Region}
Configure cfn-hup
The cfn-hup enables the existing EC2 instance to track template changes of UserData. Without it, you would manually replace your EC2 instance each time your template updates.
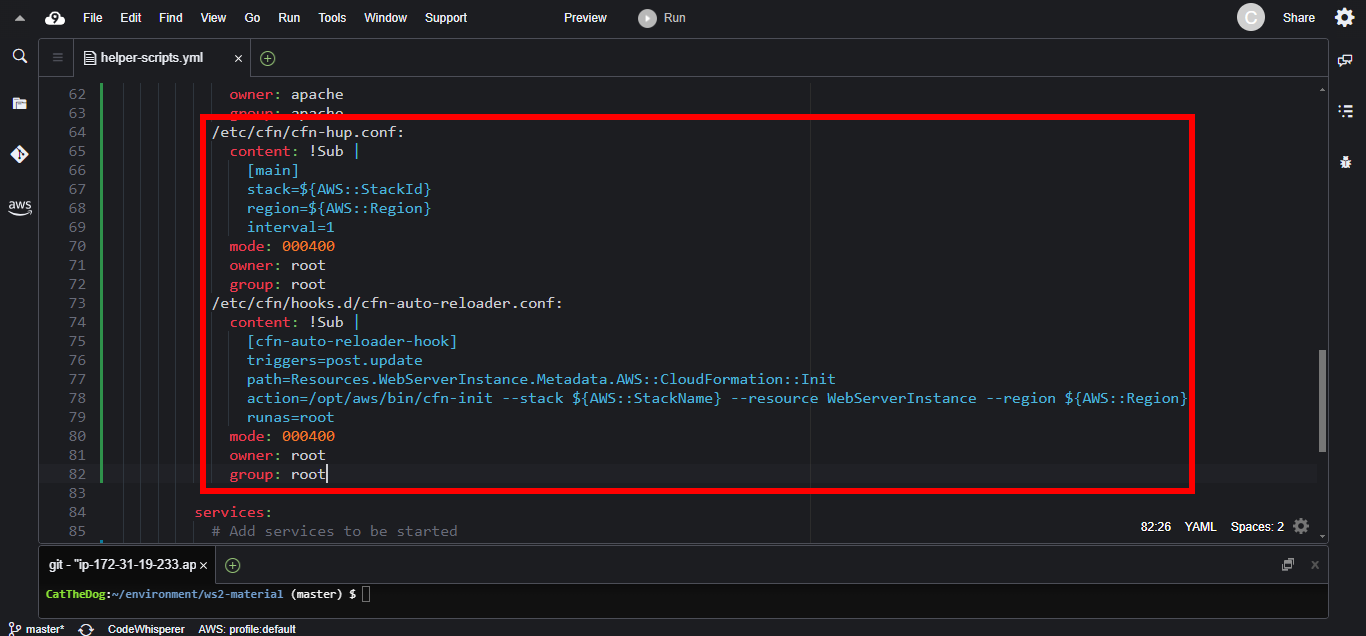
1. Add two new files in the AWS::CloudFormation::Init section.
- cfn-hup.conf: store the name and the region of the stack. The cfn-hup daemon will check for updates each 1 minute.
- cfn-auto-reloader.conf: define a hook that is periodically called when you change the AWS::CloudFormation::Init that is associated with the WebServerInstance resource.
/etc/cfn/cfn-hup.conf:
content: !Sub |
[main]
stack=${AWS::StackId}
region=${AWS::Region}
interval=1
mode: 000400
owner: root
group: root
/etc/cfn/hooks.d/cfn-auto-reloader.conf:
content: !Sub |
[cfn-auto-reloader-hook]
triggers=post.update
path=Resources.WebServerInstance.Metadata.AWS::CloudFormation::Init
action=/opt/aws/bin/cfn-init --stack ${AWS::StackName} --resource WebServerInstance --region ${AWS::Region}
runas=root
mode: 000400
owner: root
group: root
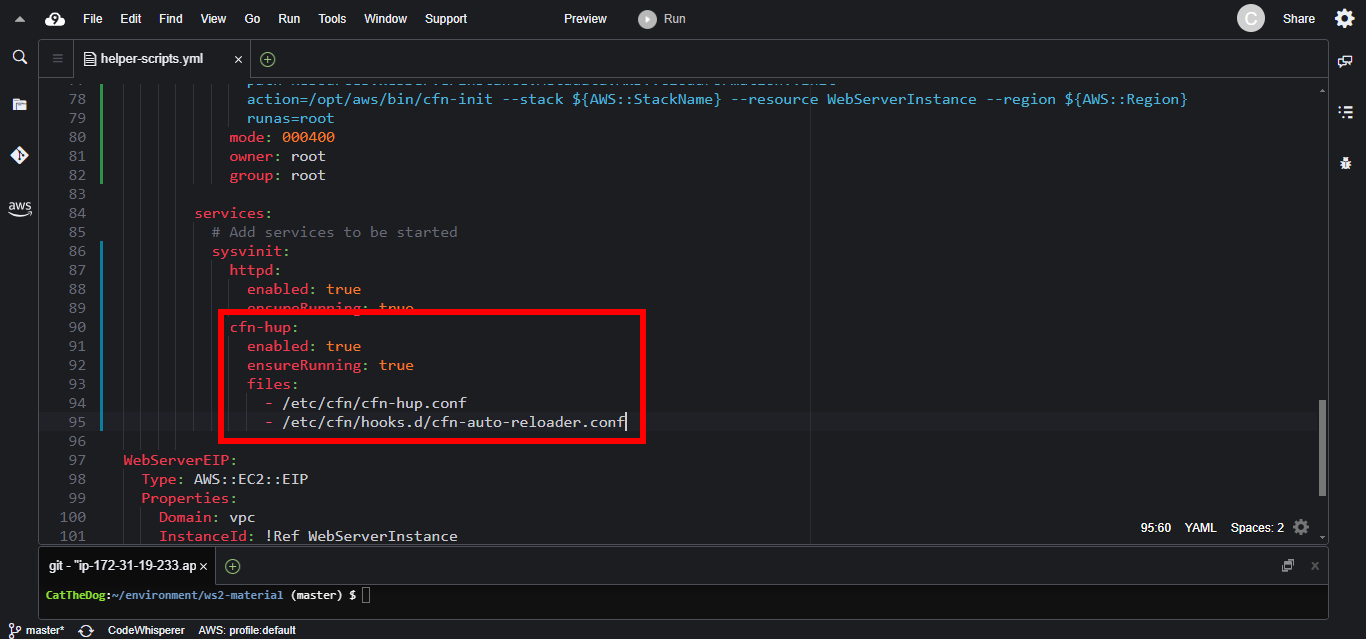
2. Enable cfn-hup in the services section. Each time the cfn-hup.conf file or the cfn-auto-reloader.conf file changes, the cfn-hup service is automatically restarted.
cfn-hup:
enabled: true
ensureRunning: true
files:
- /etc/cfn/cfn-hup.conf
- /etc/cfn/hooks.d/cfn-auto-reloader.conf
Configure cfn-signal
After your EC2 instance successfully installs all required packages and starts all services, you need something to inform CloudFormation about success status; that is the motivation for cfn-signal.
However, by default CloudFormation does not wait for cfn-signal to send it the success message. It will determine that the stack is created successfully if all the resources, including the EC2 instance, are provisioned with no error, regardless of whether the EC2 Instance has failed to start services.
To address that issue, we need to use one additional resource attribute, CreationPolicy. When attaching to the EC2 instance, it will make CloudFormation wait for a success message from instance before timeout and considering the stack creation is failed.
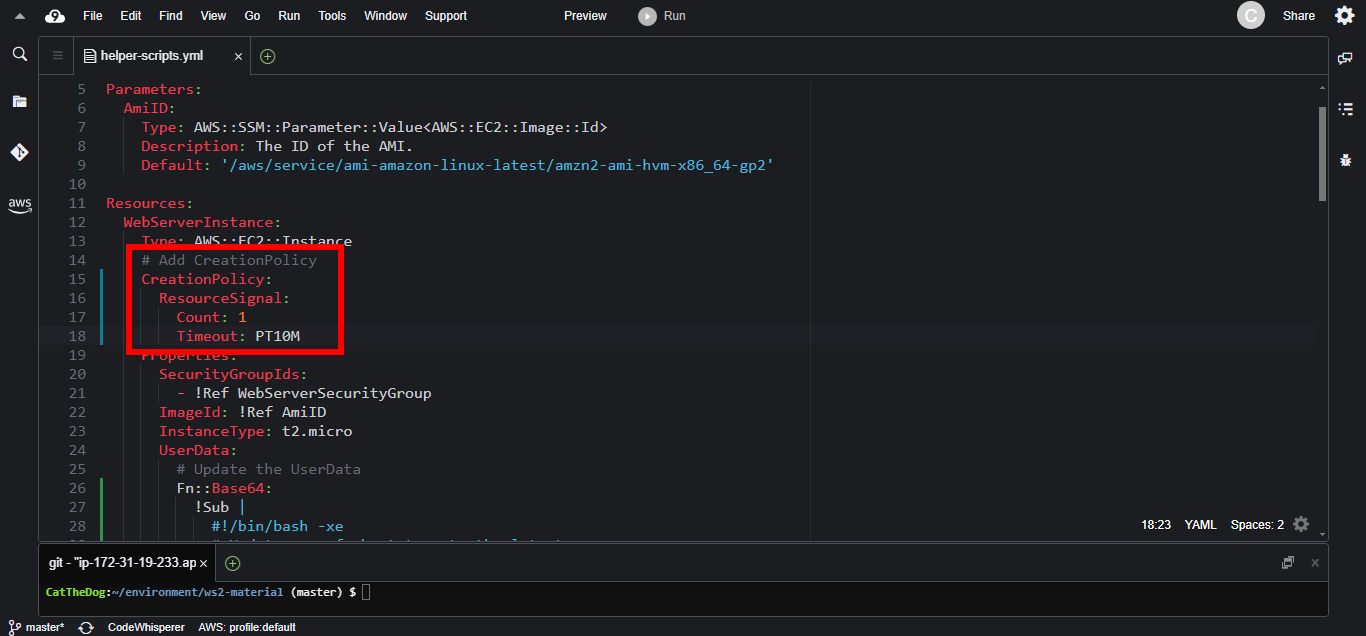
1. Add CreationPolicy to EC2 instance. CloudFormation will wait for 1 success message over 10 minutes.
CreationPolicy:
ResourceSignal:
Count: 1
Timeout: PT10M
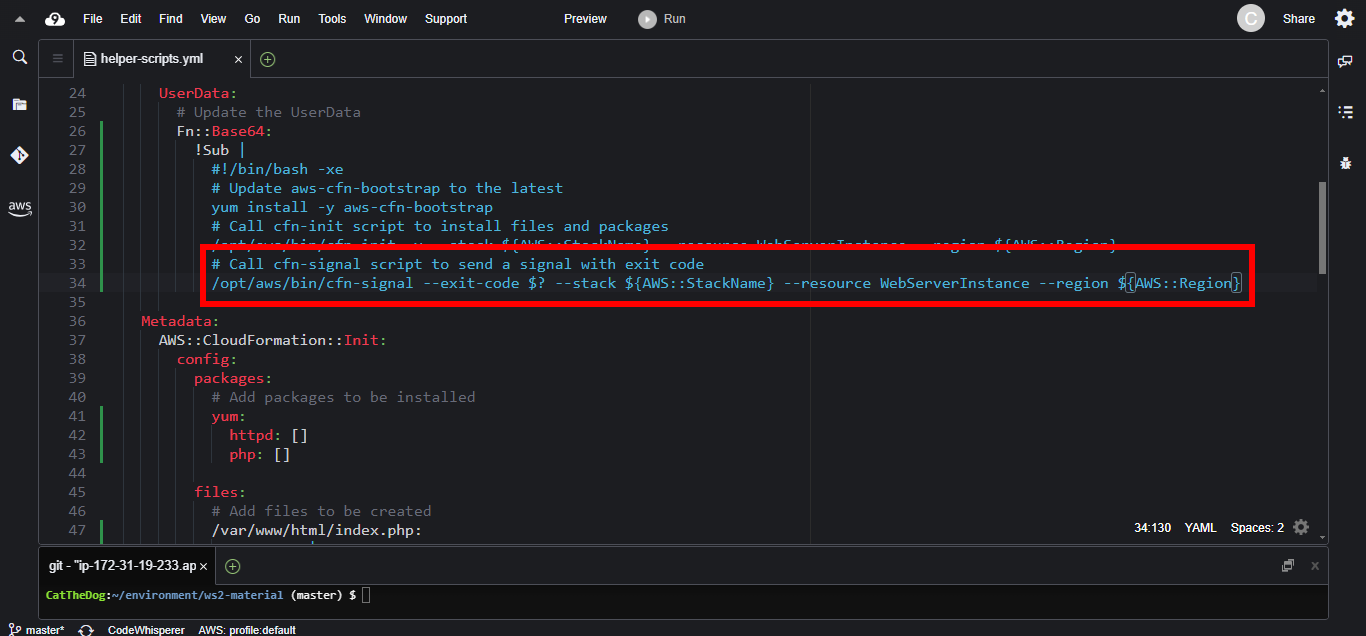
2. Add the cfn-signal to the UserData parameter.
UserData:
# Update the UserData
Fn::Base64:
!Sub |
#!/bin/bash -xe
# Update aws-cfn-bootstrap to the latest
yum install -y aws-cfn-bootstrap
# Call cfn-init script to install files and packages
/opt/aws/bin/cfn-init -v --stack ${AWS::StackName} --resource WebServerInstance --region ${AWS::Region}
# Call cfn-signal script to send a signal with exit code
/opt/aws/bin/cfn-signal --exit-code $? --stack ${AWS::StackName} --resource WebServerInstance --region ${AWS::Region}
Create and update stack
1. Execute the command below to create a new stack.
cd ~/environment/ws2-material/workshop/fundamental
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name helper-scripts --template-body file://helper-scripts.yml
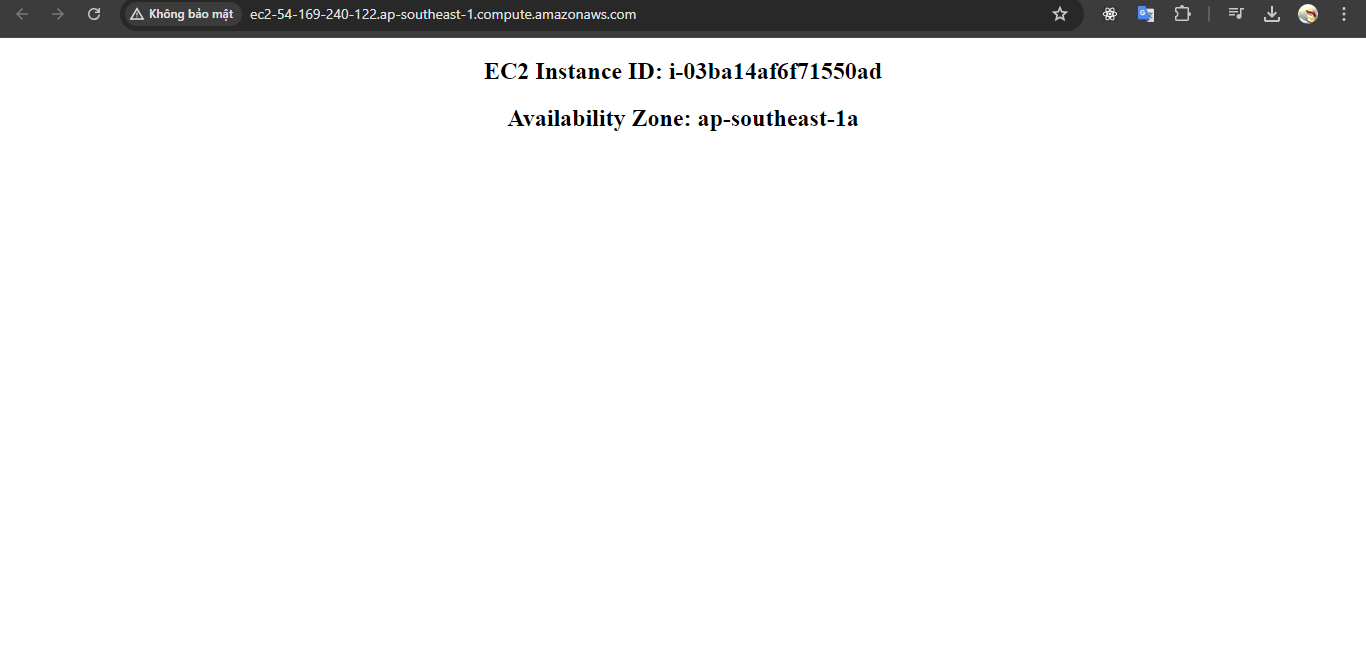
2. Once stack is created successfully, open the EC2 instance’ IP or DNS name to see the result.
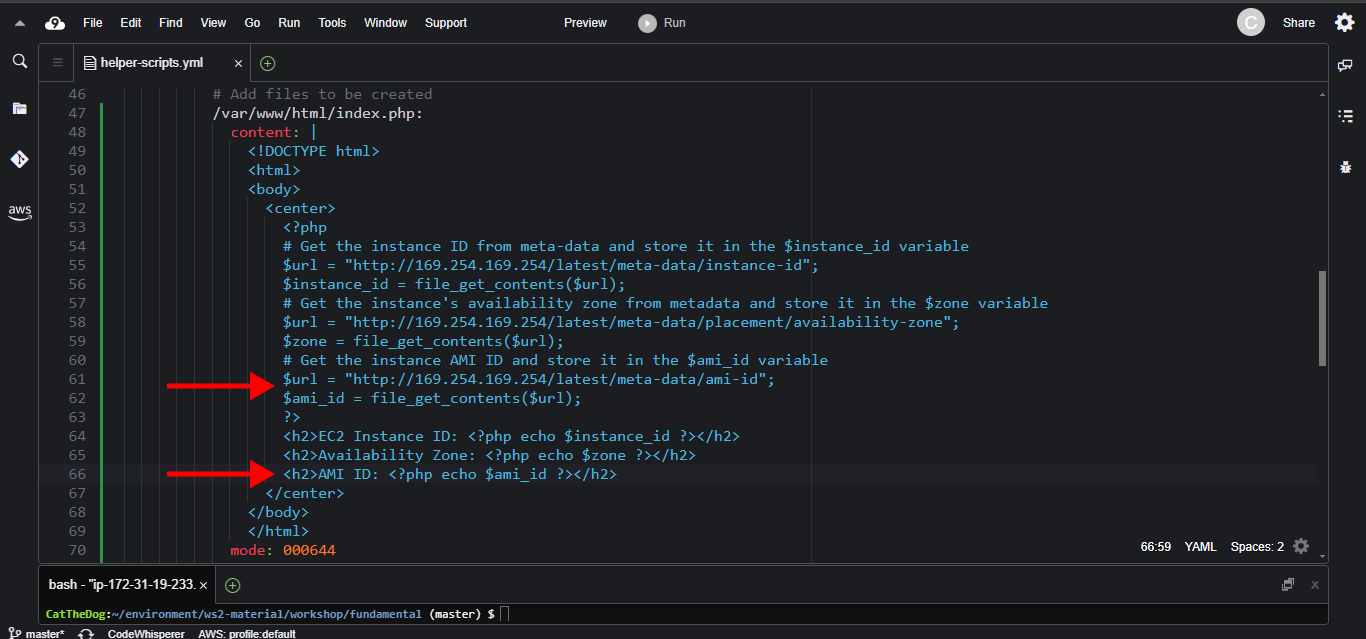
3. For testing cfn-hup, update the the template to:
/var/www/html/index.php:
content: |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<center>
<?php
# Get the instance ID from meta-data and store it in the $instance_id variable
$url = "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id";
$instance_id = file_get_contents($url);
# Get the instance's availability zone from metadata and store it in the $zone variable
$url = "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone";
$zone = file_get_contents($url);
# Get the instance AMI ID and store it in the $ami_id variable
$url = "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ami-id";
$ami_id = file_get_contents($url);
?>
<h2>EC2 Instance ID: <?php echo $instance_id ?></h2>
<h2>Availability Zone: <?php echo $zone ?></h2>
<h2>AMI ID: <?php echo $ami_id ?></h2>
</center>
</body>
</html>
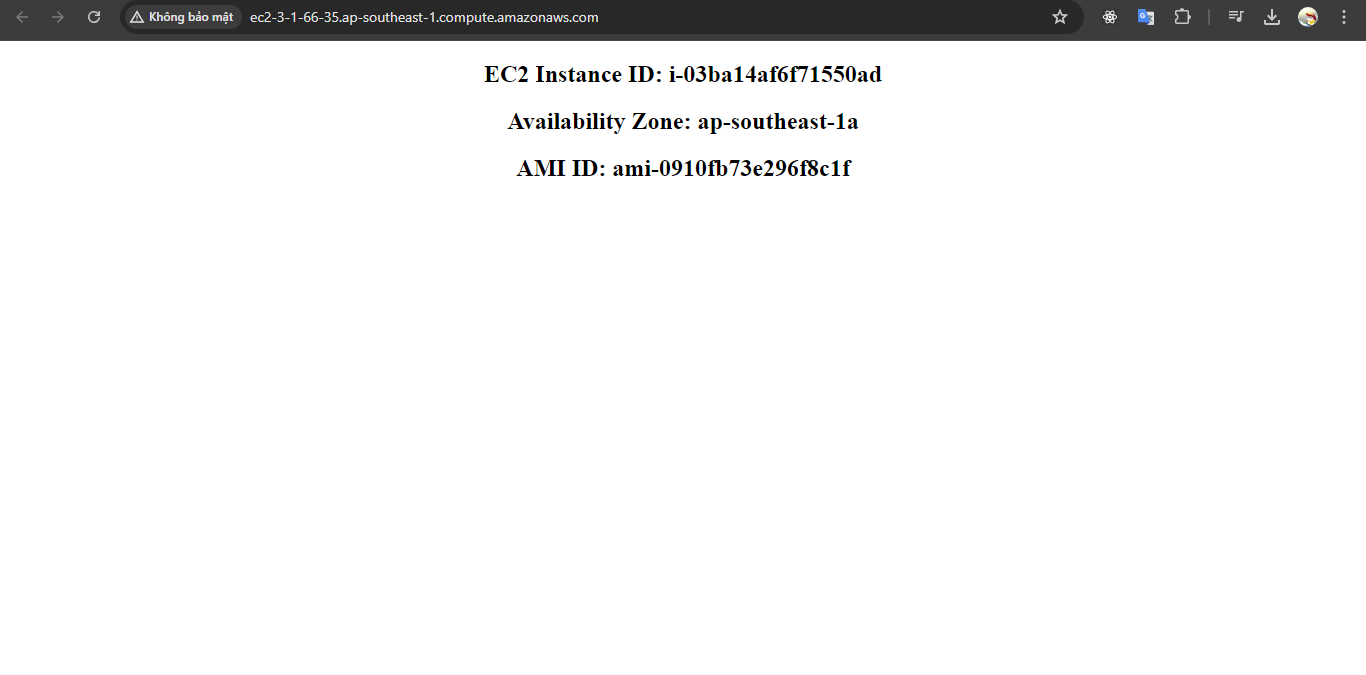
4. Execute the command below to update the stack.
aws cloudformation update-stack --stack-name helper-scripts --template-body file://helper-scripts.yml
5. Open browser to see the result.
Cleaning up
Run the delete command to delete your stack:
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name helper-scripts