Pseudo parameters
What is Pseudo Parameter ?
Pseudo Parameter is a parameter that is predefined by AWS CloudFormation. You don’t need to declare it in your template. Use it the same as you would a parameter, as the argument for the Ref intrinsic function
In AWS, we have several pseudo parameters, such as:
AWS::AccountId: Returns the AWS account ID of the account in which the stack is being created, such as 123456789012.
AWS::Region: Returns a string representing the Region in which the encompassing resource is being created, such as us-west-2.
AWS::Partition: Returns the partition that the resource is in. For standard AWS Regions, the partition is aws; for the China (Beijing and Ningxia) region is aws-cn, and for the AWS GovCloud (US-West) region is aws-us-gov.
And we will use the Ref function when working with those parameters. For instance, !Ref AWS::AccountId and !Ref AWS::Region return the AccountId and the region name of the stack off of your template.
Examining the illustration
In the following example, we will create a parameter in the AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store, which is a storage of configuration data for our resources, such as database connection strings, secret key, etc. Then we build a Lambda function that reads the parameter in the store and output it when executed.
The first thing we need to do is to define a CloudFormation parameter which is used as the value of our parameter in the Parameter Store.
Parameters:
DatabaseUsername:
AllowedPattern: ^[a-z0-9]{5,12}$
Type: String
Default: alice
Description: Value to be used with the dbUsername SSM parameter.
Next, we add a new System Manager parameter which has the type AWS::SSM::Parameter, then we pass the DatabaseUsername CloudFormation parameter to our resource.
Resources:
BasicParameter:
Type: AWS::SSM::Parameter
Properties:
Name: dbUsername
Type: String
Value: !Ref DatabaseUsername
Description: SSM Parameter for database username.
For Lambda function to read the parameter, it must be assigned an IAM role with least privilege access to the parameter.
DemoRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: ssm-least-privilege
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: ssm:GetParameter
Resource: !Sub 'arn:${AWS::Partition}:ssm:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:parameter/${BasicParameter}'
As you can see, we attach a policy that allows our lambda function to access only the parameter with a specific ARN rather than all resources, meeting the principle of least privilege. ARN is also the place where pseudo parameters perform their tasks; in the snippet above, we combine AWS::Partition, AWS::Region, AWS::AccountId and BasicParameter to form the ARN of the parameter.
According to the AWS::SSM::Parameter documentation , if we use !Sub {BasicParameter} or !Ref BasicParameter, we will get a physical name of BasicParameter. So that the parameter ARN will be resolved as:
arn:aws:ssm:ap-southeast1:123456789012:parameter/BasicParameter-ABCNPH3XCAO6
Finally, we declare a lambda function and attach the role to it. Our function use Python to access the parameter via the boto3 library and logs the value of it.
DemoLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Handler: index.lambda_handler
Role: !GetAtt DemoRole.Arn
Runtime: python3.8
Code:
ZipFile: |
import boto3
client = boto3.client('ssm')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
response = client.get_parameter(Name='dbUsername')
print(f'SSM dbUsername parameter value: {response["Parameter"]["Value"]}')
Reinforce your understanding
1. Open Cloud9 then find ~/environment/ws2-material/workshop/fundamental/pseudo-parameters.yml.
2. Copy and paste the snippet below to add the CloudFormation parameter DatabaseUsername.
Parameters:
DatabaseUsername:
AllowedPattern: ^[a-z0-9]{5,12}$
Type: String
Default: alice
Description: Value to be used with the dbUsername SSM parameter.
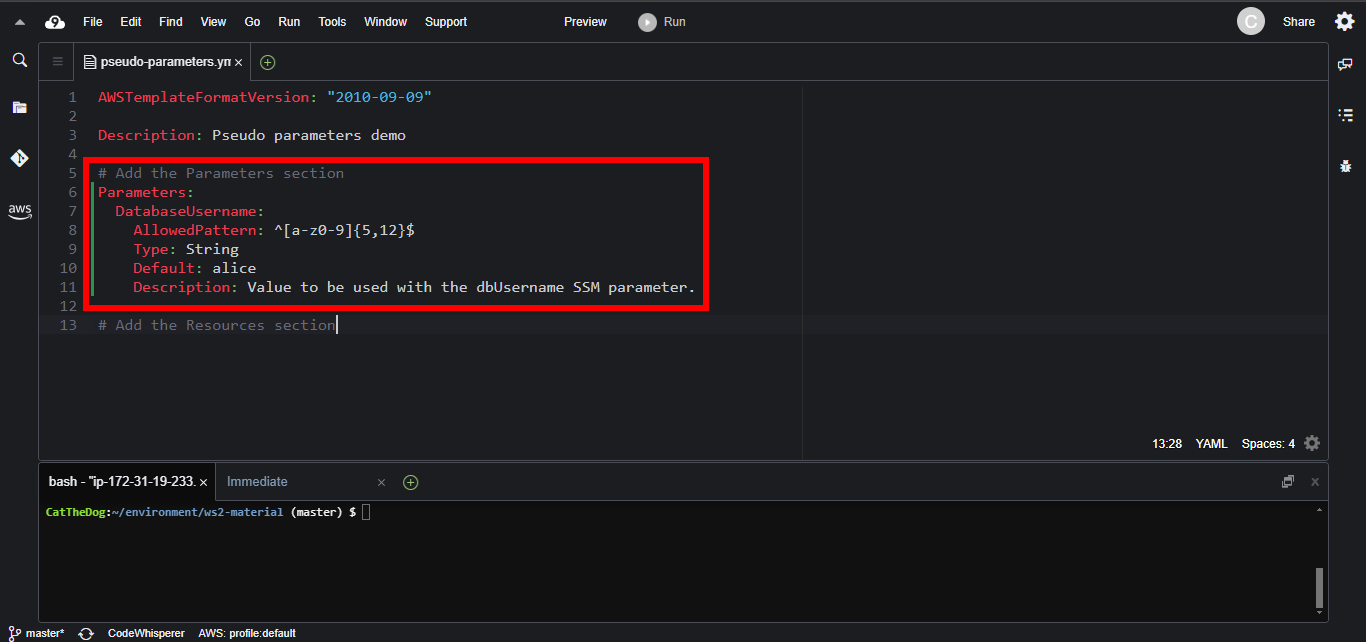
3. Add the system manager parameter BasicParameter.
Resources:
BasicParameter:
Type: AWS::SSM::Parameter
Properties:
Name: dbUsername
Type: String
Value: !Ref DatabaseUsername
Description: SSM Parameter for database username.
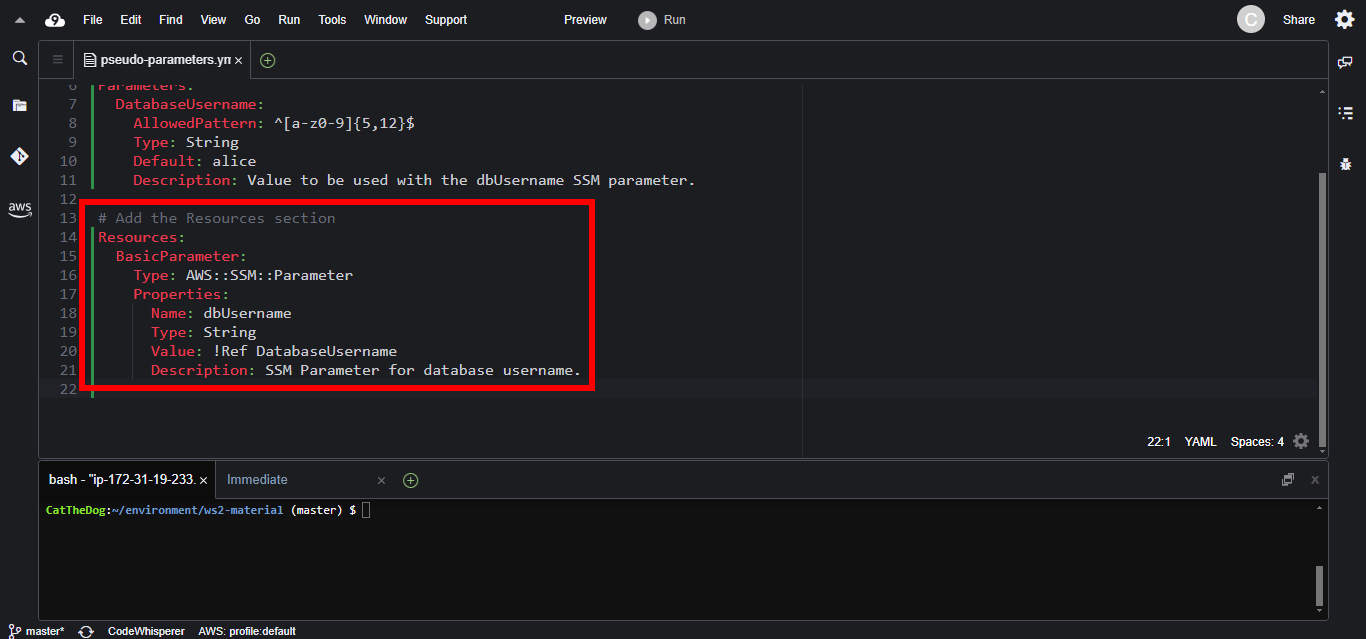
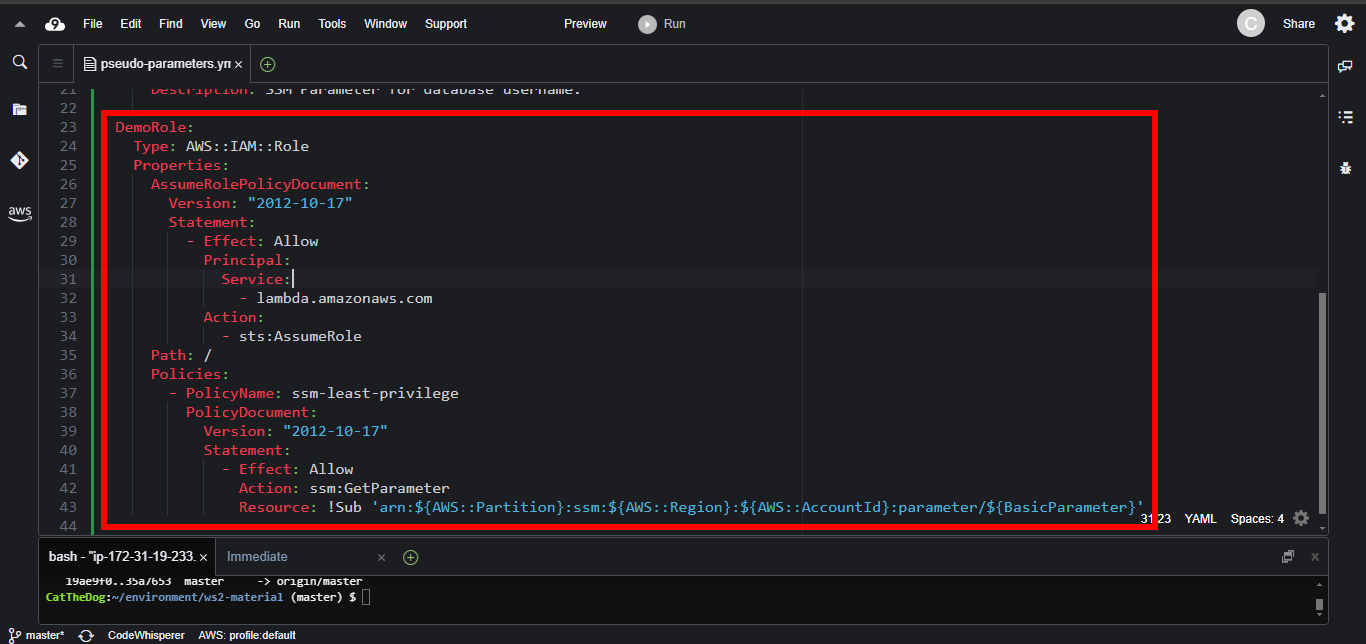
4. Add the IAM role.
DemoRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: ssm-least-privilege
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: ssm:GetParameter
Resource: !Sub 'arn:${AWS::Partition}:ssm:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:parameter/${BasicParameter}'
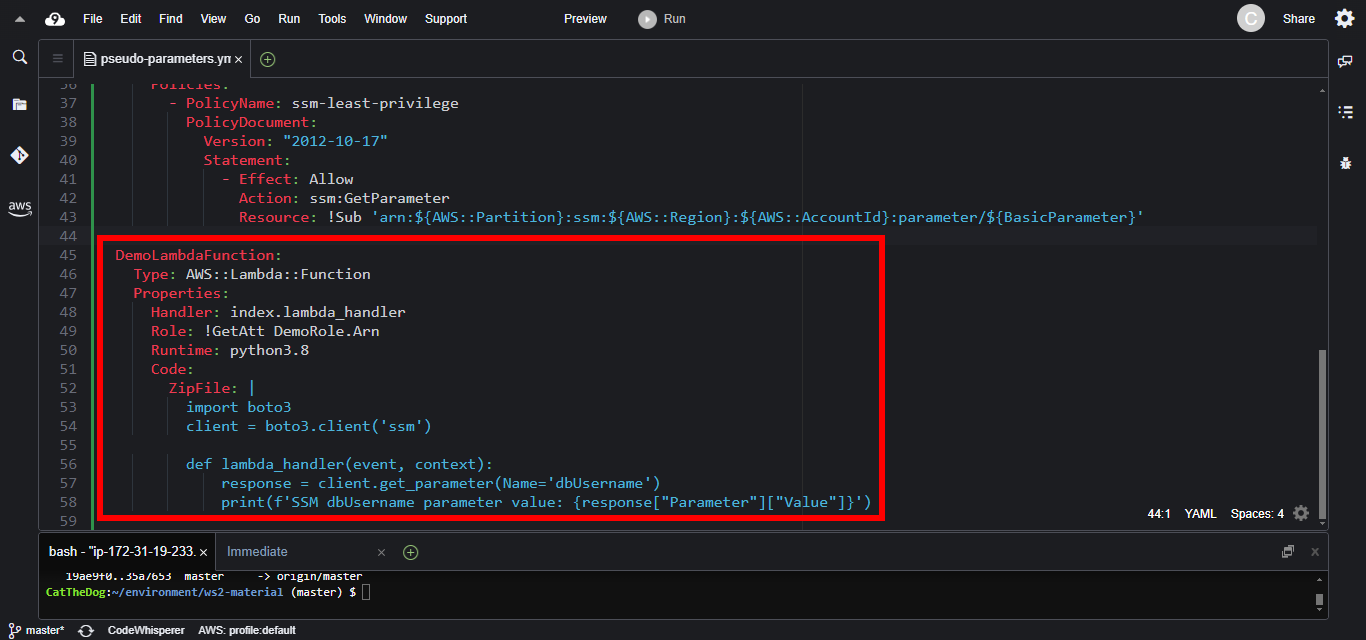
5. Add the Lambda function.
DemoLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Handler: index.lambda_handler
Role: !GetAtt DemoRole.Arn
Runtime: python3.8
Code:
ZipFile: |
import boto3
client = boto3.client('ssm')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
response = client.get_parameter(Name='dbUsername')
print(f'SSM dbUsername parameter value: {response["Parameter"]["Value"]}')
6. Run the command to create a new stack.
cd ~/environment/ws2-material/workshop/fundamental
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name pseudo-parameters --template-body file://pseudo-parameters.yml --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
The argument –capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM allows CloudFormation to create IAM role.
7. Once stack created successfully, navigate to the Lambda function.
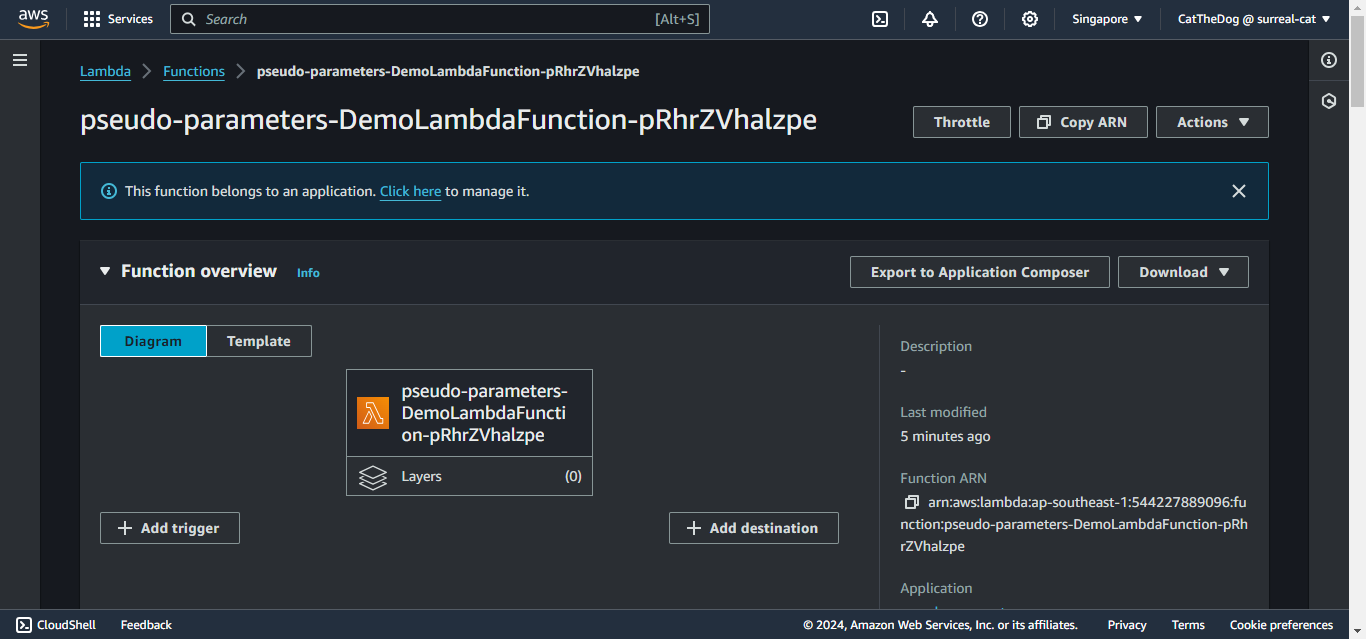
8. To trigger the function, scroll down and click on Test.
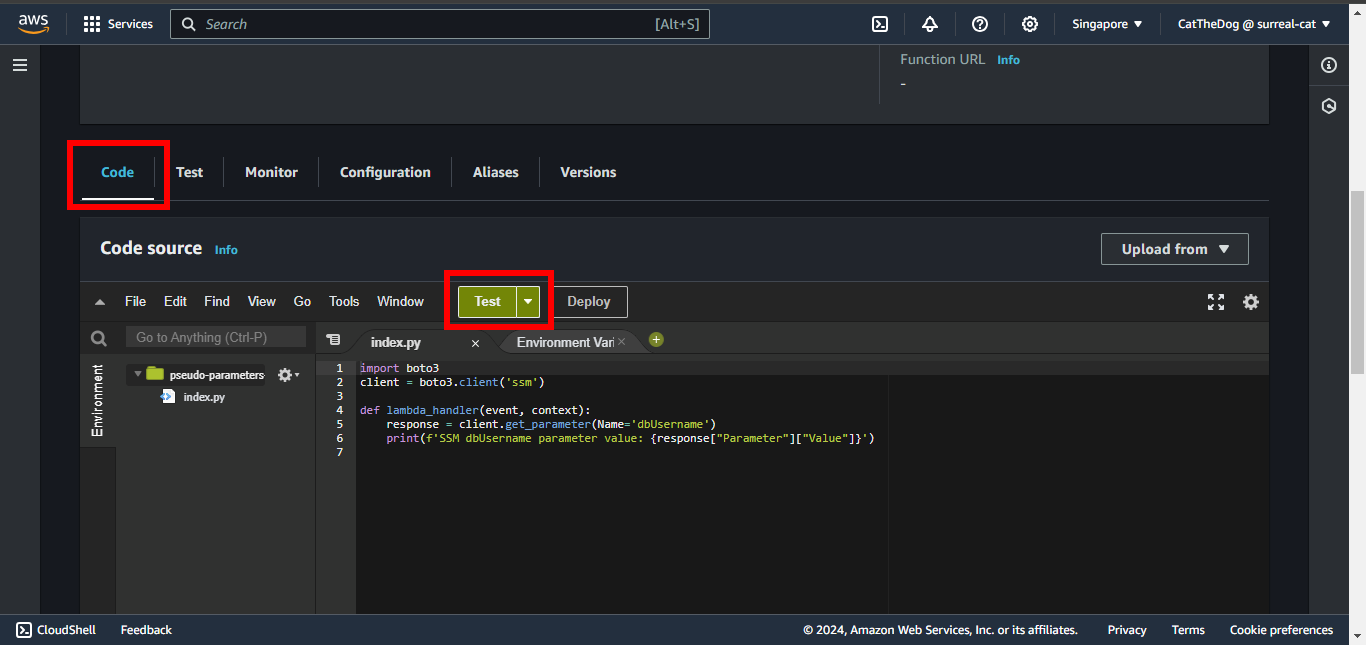
9. Enter my-event-name for Event name, then click on Invoke.
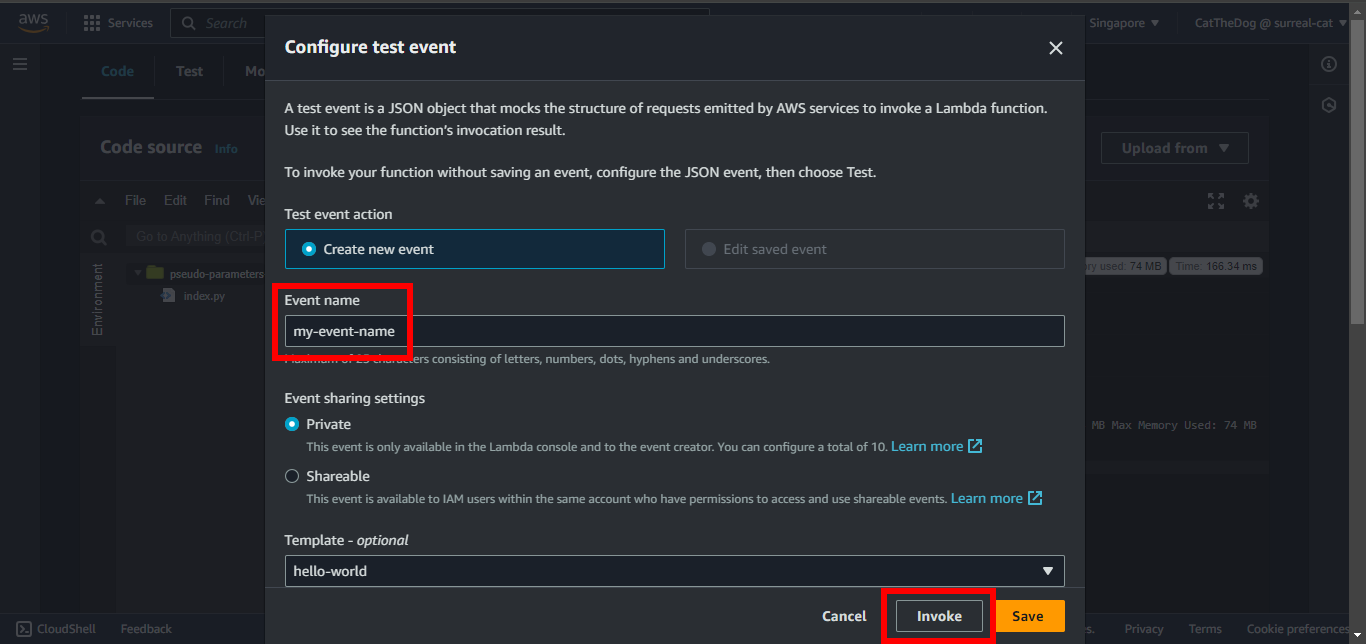
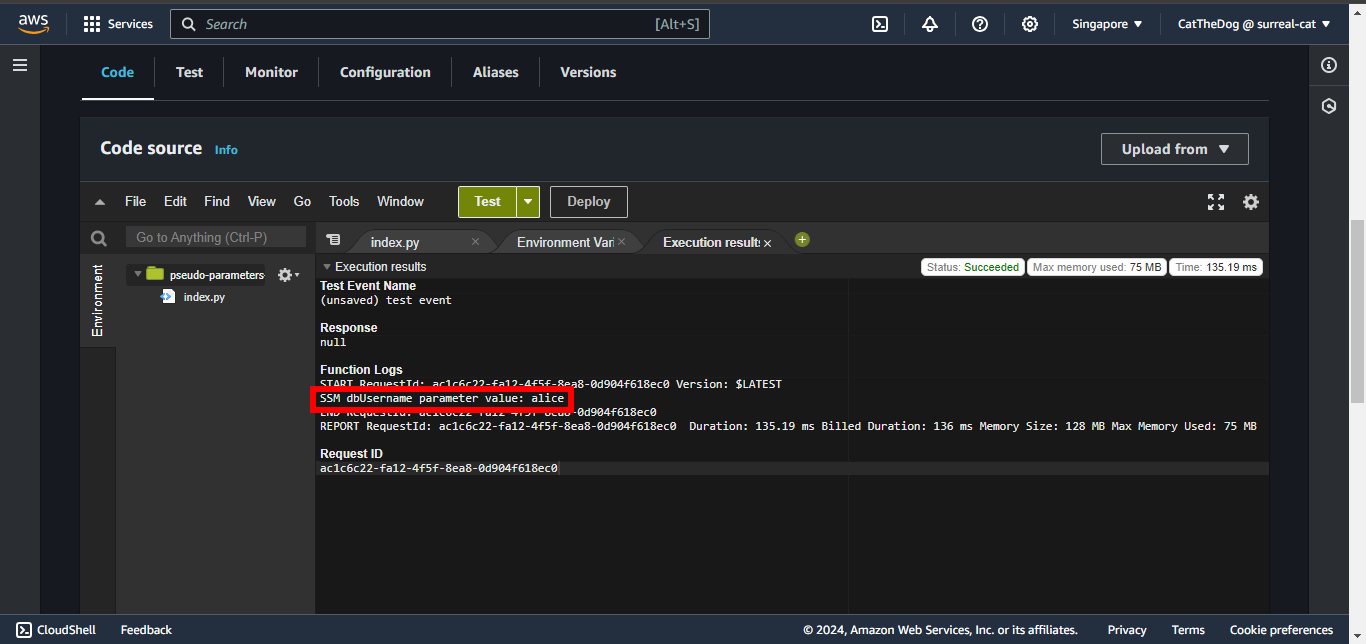
10. Validate the data logged by function.
Cleaning up
Run the delete command to delete your stack:
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name pseudo-parameters