Template overview
What is the CloudFormation template ?
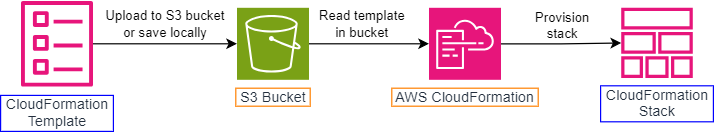
A template is a text file that serves as a blueprint for your infrastructure, defining the resources ,their configuration and dependencies. When you create or update a stack, CloudFormation provisions and configures the resources specified in the template.
So let we discuss the common concepts of the CloudFormation template:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion (optional): identifies the capabilities of the template. The current only accepted value is “2010-09-09”.
Description (optional): enables you to include comments about your template.
Metadata (optional): enables you to include additional information about the template or resources, such as resources description or configuration settings.
Parameters (optional): defines parameters that can be used to customize resources when creating or updating the stack.
Rules (Optional): validates parameters passed in during a stack creation or stack update.
Mappings (Optional): matches a key to a corresponding set of named values.
Conditions (Optional): defines conditional expressions that can be used to control the creation and update of resources based on certain criteria or parameter values.
Transform (Optional): defines one or more macros(A reusable piece of CloudFormation configuration) that CloudFormation should use to process before creating or updating the stack.
Resources (REQUIRED): declares the AWS resources that you want to create.
Outputs (Optional): defines the output values that can be returned or referenced by other stacks.
What is the CloudFormation stack ?
A stack is representation of collections of AWS resources that you can manage as a single unit. A stack is created based on a template.
CloudFormation will create, update and delete a stack in its entirety. When any failure in the stack creation or stack update, CloudFormation will roll it back to the previous state, keeping it always in a consistent state and reducing the risk of manual error.