Define the Task Execution Role
Task Role vs. Task Execution Role
Amazon ECS utilizes two distinct IAM roles for tasks: the Task Role and the Task Execution Role. Understanding their different purposes is crucial.
Task Role (Permissions for your Application)
This IAM role is associated with your Amazon ECS tasks themselves. The permissions granted in this role are assumed by the application code running inside your containers. This allows your application to directly interact with other AWS services, such as reading from an S3 bucket or writing to a DynamoDB table. A Task Role is required whenever your application code needs to make AWS API calls.
Task Execution Role (Permissions for ECS to Prepare your Task)
This IAM role grants permissions to the Amazon ECS container agent and AWS Fargate agent to perform actions on your behalf. These actions are necessary to prepare and run your task, such as pulling container images or sending logs.
The Task Execution Role is required for tasks, particularly when:
- Pulling a container image from a private Amazon ECR repository.
- Sending container logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
You can have multiple Task Execution Roles tailored for different needs, but typically a standard one is used for common operations like ECR access and CloudWatch logging.
Create Task Execution Role
We will create an IAM Task Execution Role that grants the Amazon ECS agent (and AWS Fargate agent) the necessary permissions to launch and manage our tasks. This role specifically needs permissions for the following actions:
- Pulling container images from Amazon ECR
- Retrieving secrets from AWS Secrets Manager (for injecting into tasks)
- Pushing container logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs
- Creating Amazon CloudWatch log groups (if they don’t already exist)
Important Security Note: In this workshop, for simplicity, we will attach AWS-managed policies to this role. However, in a production environment, you should always create custom IAM policies that grant only the specific permissions required (the principle of least privilege). This minimizes potential security risks.
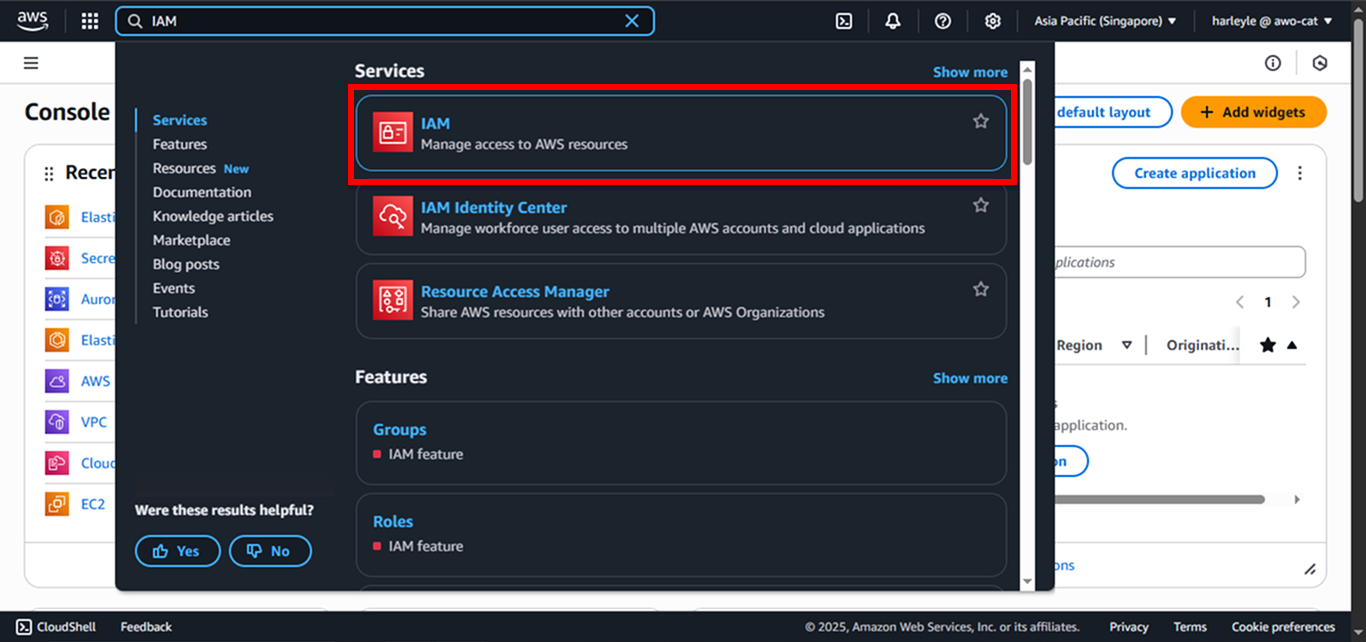
1. Navigate to IAM:
- In the AWS Console search bar, type
IAM - Select IAM from the dropdown
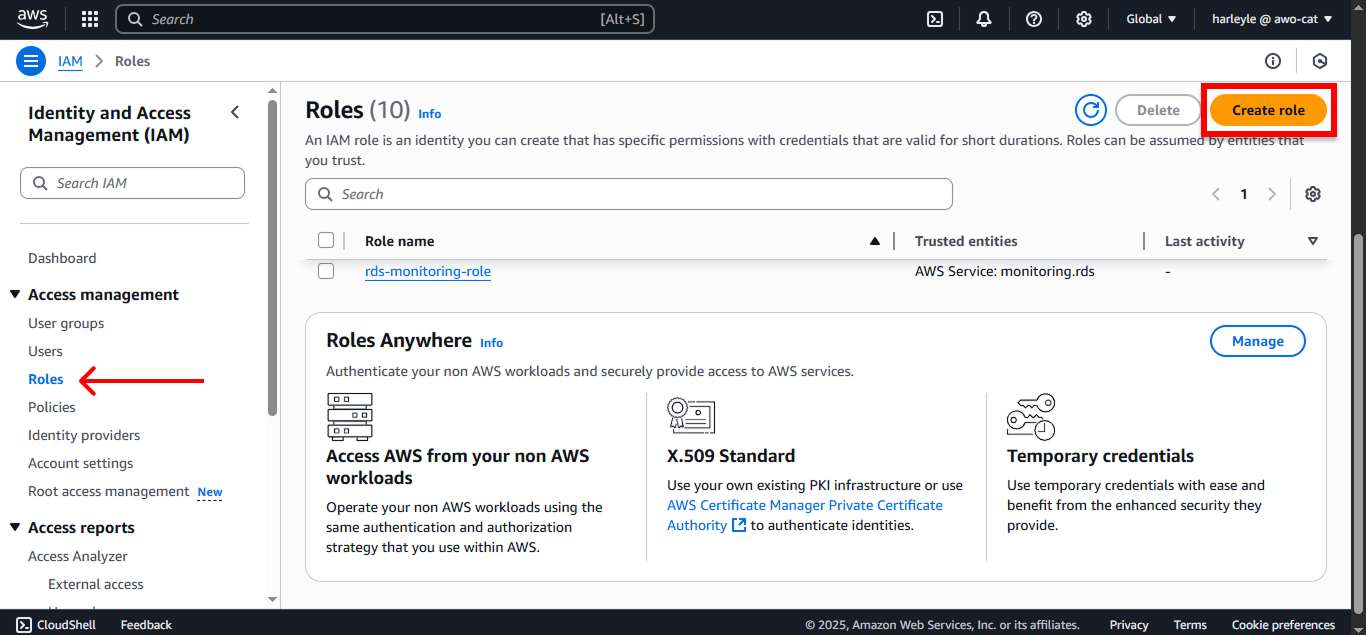
2. In the IAM Dashboard, select Roles from the left navigation panel, then click Create role.
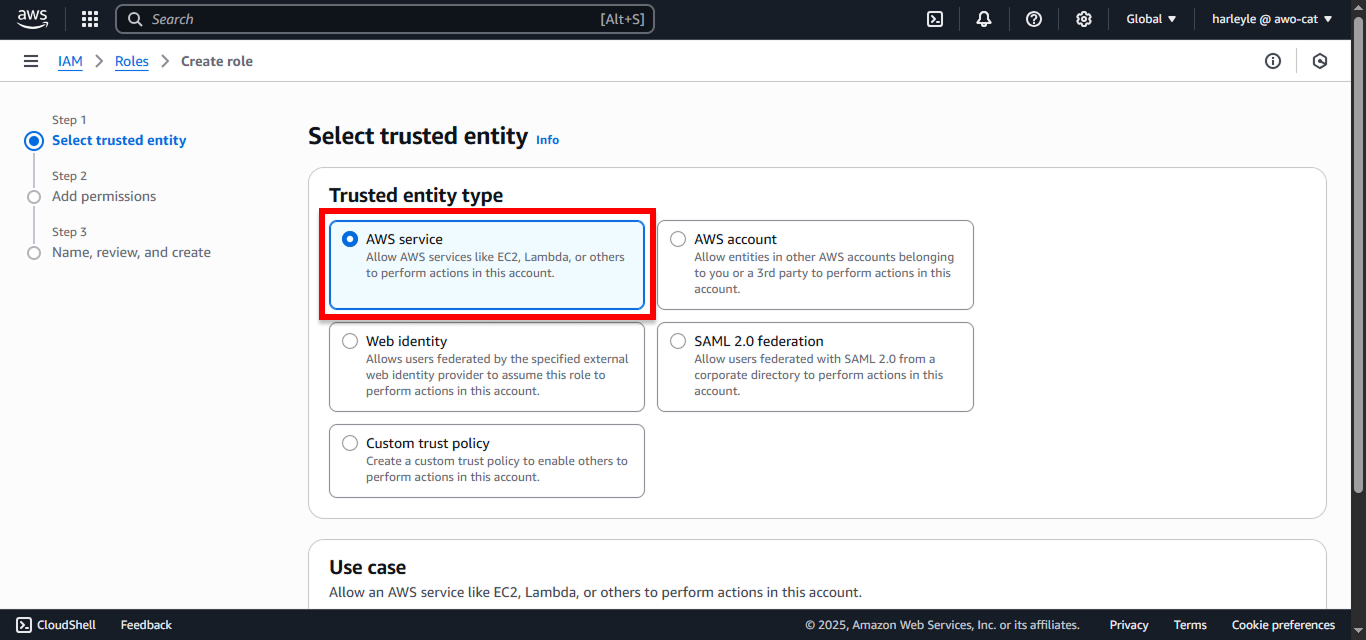
3. Configure the trusted entity:
- Trusted entity type: Select AWS service
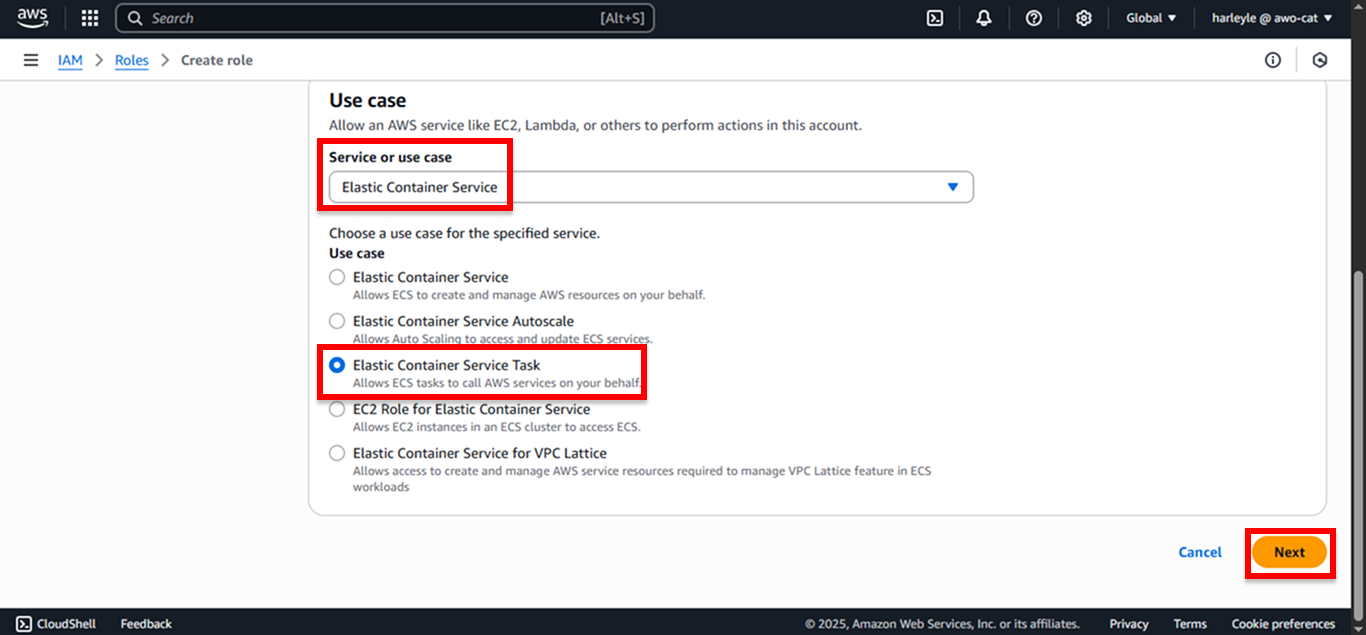
- Service or use case: Select Elastic Container Service
- Use case: Select Elastic Container Service Task
- Click Next
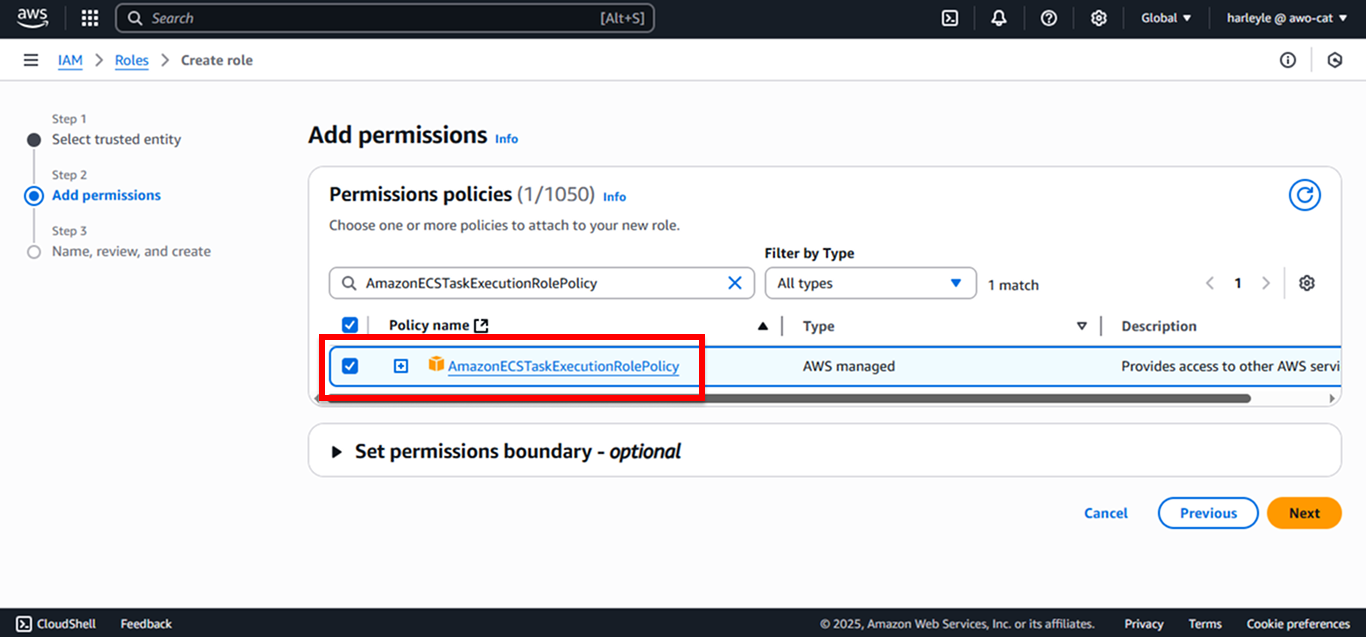
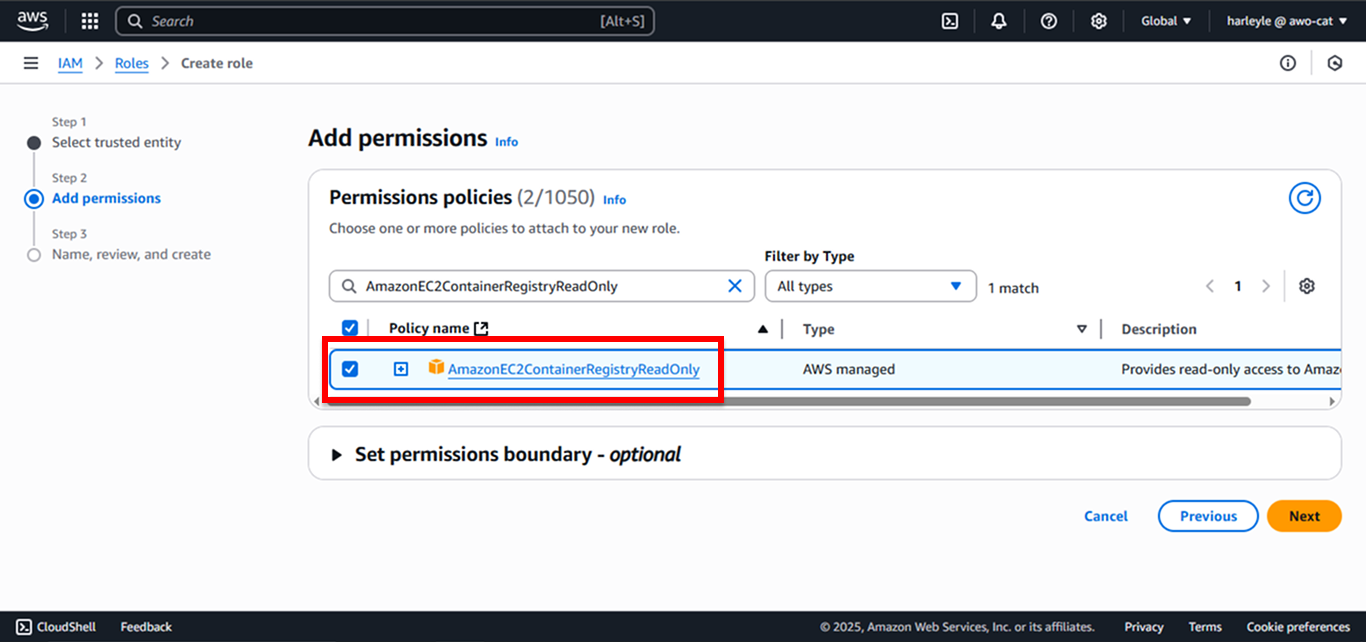
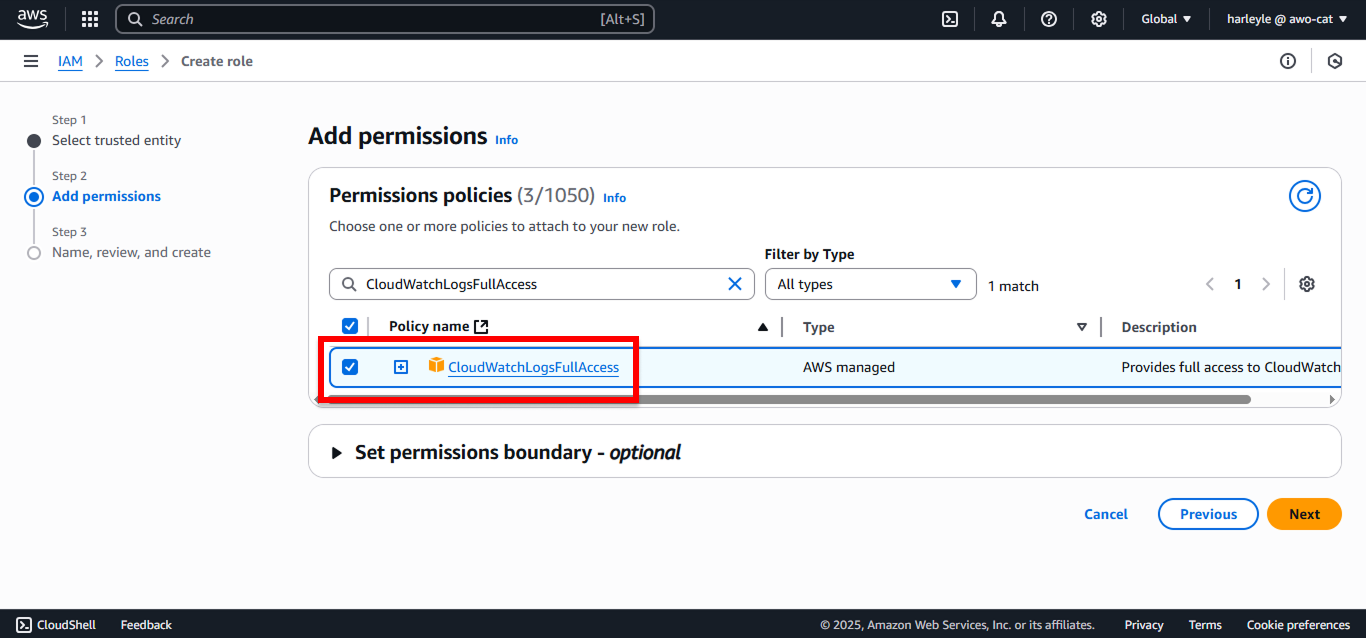
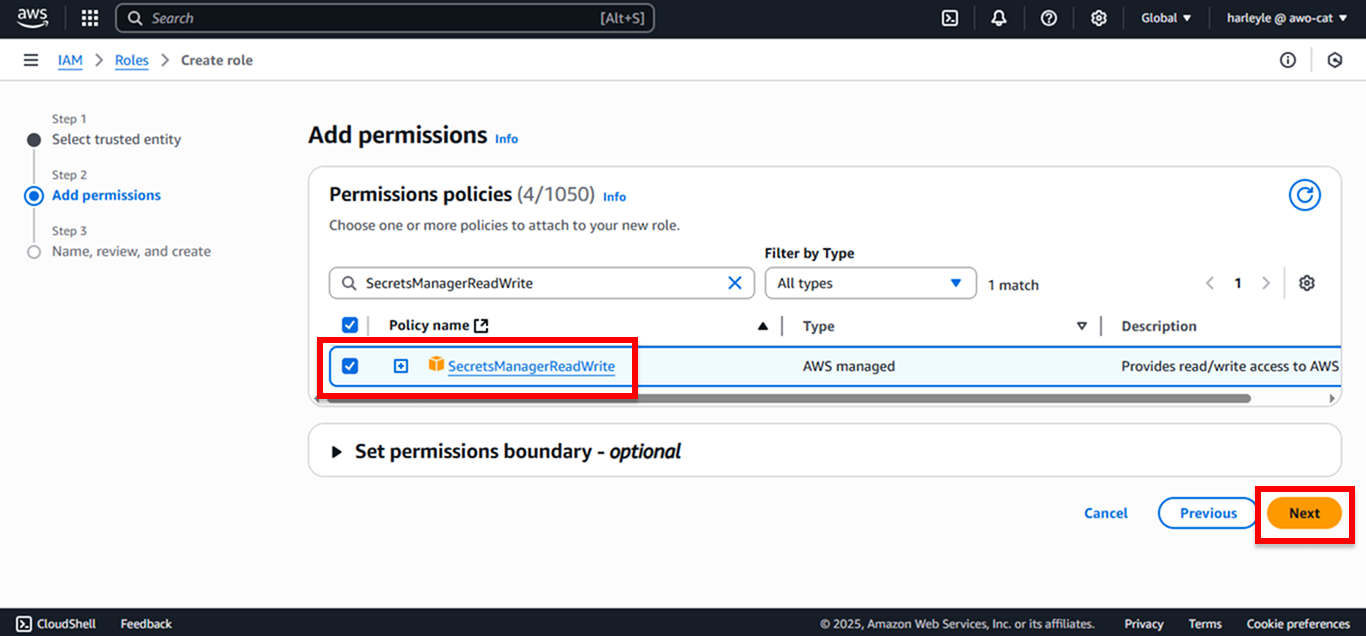
4. Attach the required policies by searching for and selecting each one:
- AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy (Essential for ECS task execution)
- AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly (For pulling images from ECR)
- CloudWatchLogsFullAccess (For sending logs to CloudWatch)
- SecretsManagerReadWrite (For retrieving database connection string)
After selecting all four policies, click Next.
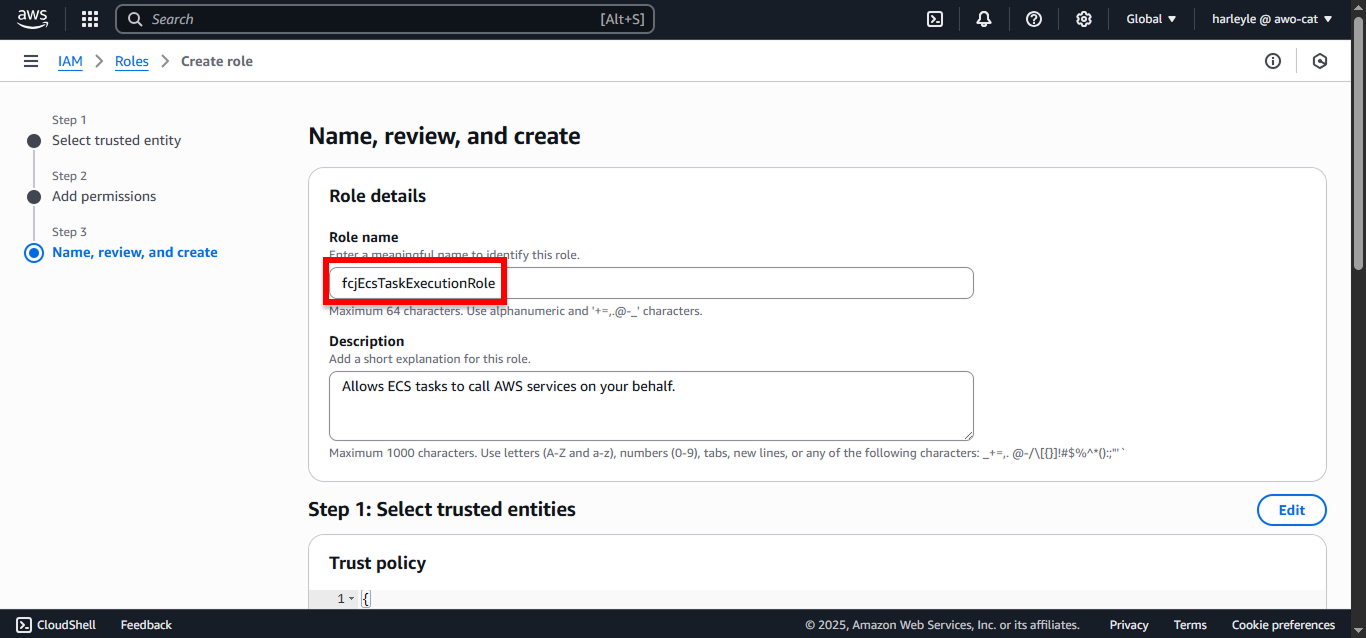
5. Configure the role details:
- Role name: Enter
fcjEcsTaskExecutionRole - Review the attached policies to ensure all four are included
- Click Create role
6. Verify creation: Confirm that the fcjEcsTaskExecutionRole appears in your roles list with all four policies attached.
Your Task Execution Role is now ready to be used in your ECS task definitions. This role provides the necessary permissions for Fargate to manage your containerized applications.
