Create Secret for Database Connection String
Secrets Manager Overview
AWS Secrets Manager is a service that helps you protect access to your applications, services, and IT resources. It enables you to easily manage, retrieve, and rotate database credentials, application credentials, OAuth tokens, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycles. Many AWS services can store and use secrets managed by Secrets Manager.
Using Secrets Manager significantly improves your security posture. Instead of hardcoding sensitive credentials in your application’s source code, you store them securely in Secrets Manager. This practice helps prevent credentials from being compromised if someone inspects your application or its components. Your application can then make a runtime call to the Secrets Manager service to retrieve these credentials dynamically when needed.
In this workshop, we will create a secret containing our database’s connection details (like the endpoint and credentials). We’ll use this secret for two main purposes:
- Injecting into ECS Tasks: The secret will be injected into our running containers. This allows the application within the containers to establish a connection to the database for reading/writing data and, initially, for applying database migrations. This replaces the less secure method of using environment variables for sensitive data.
- Injecting into AWS CodeBuild: The secret will also be used by AWS CodeBuild projects, specifically for running database migrations during our CI/CD pipeline. We will configure this in a later section.
Create Secret
1. Wait for database availability: Ensure your RDS database shows “Available” status. In the RDS Dashboard, click on your fcj-db database instance.
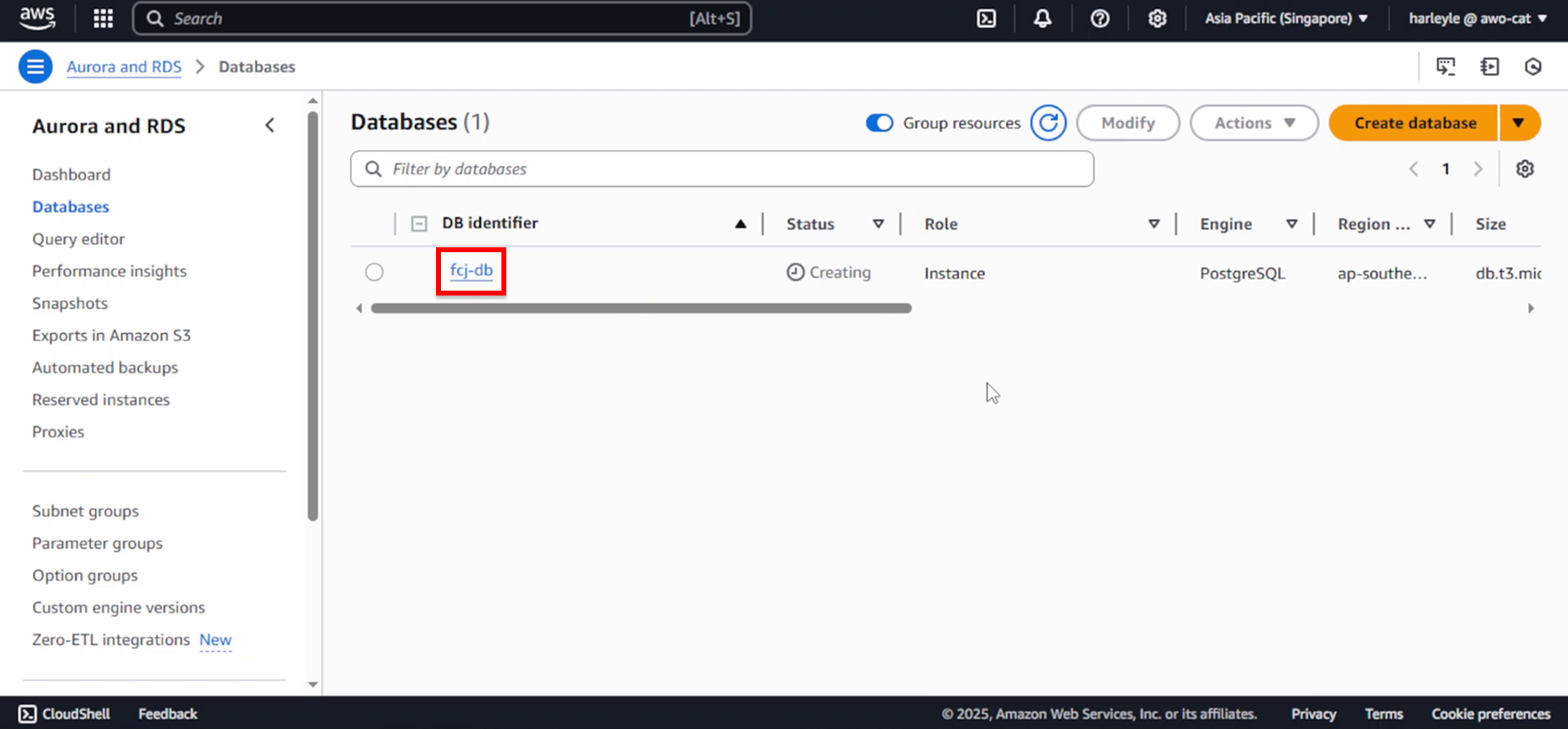
2. Copy the database endpoint:
- Under Connectivity & security, locate and copy your database’s Endpoint
- Save this endpoint as you’ll need it in the next step
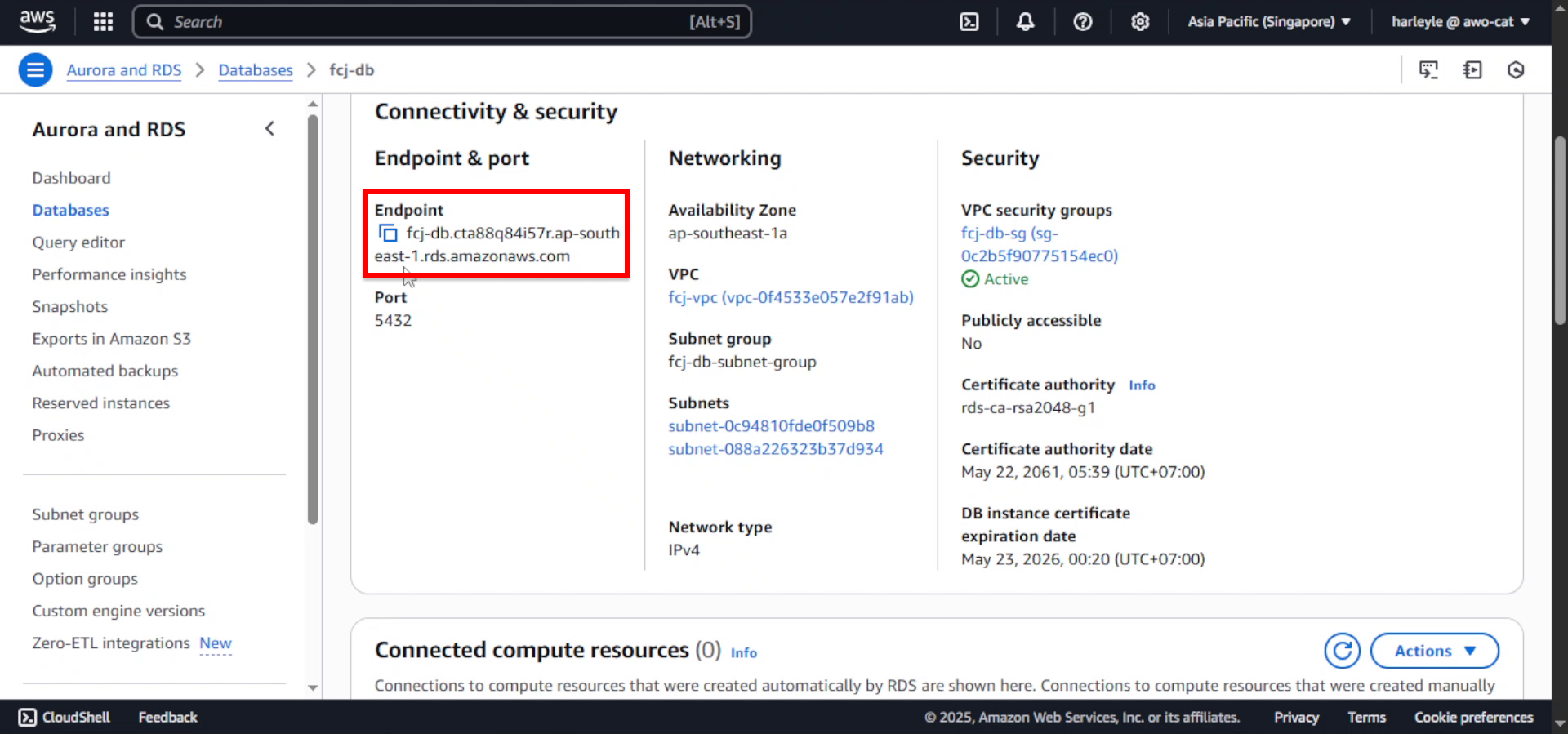
3. Navigate to AWS Secrets Manager:
- In the AWS Console search bar, type “Secrets Manager”
- Select AWS Secrets Manager from the dropdown
4. Click Store a new secret.
5. Configure the secret type:
- Secret type: Select Other type of secret
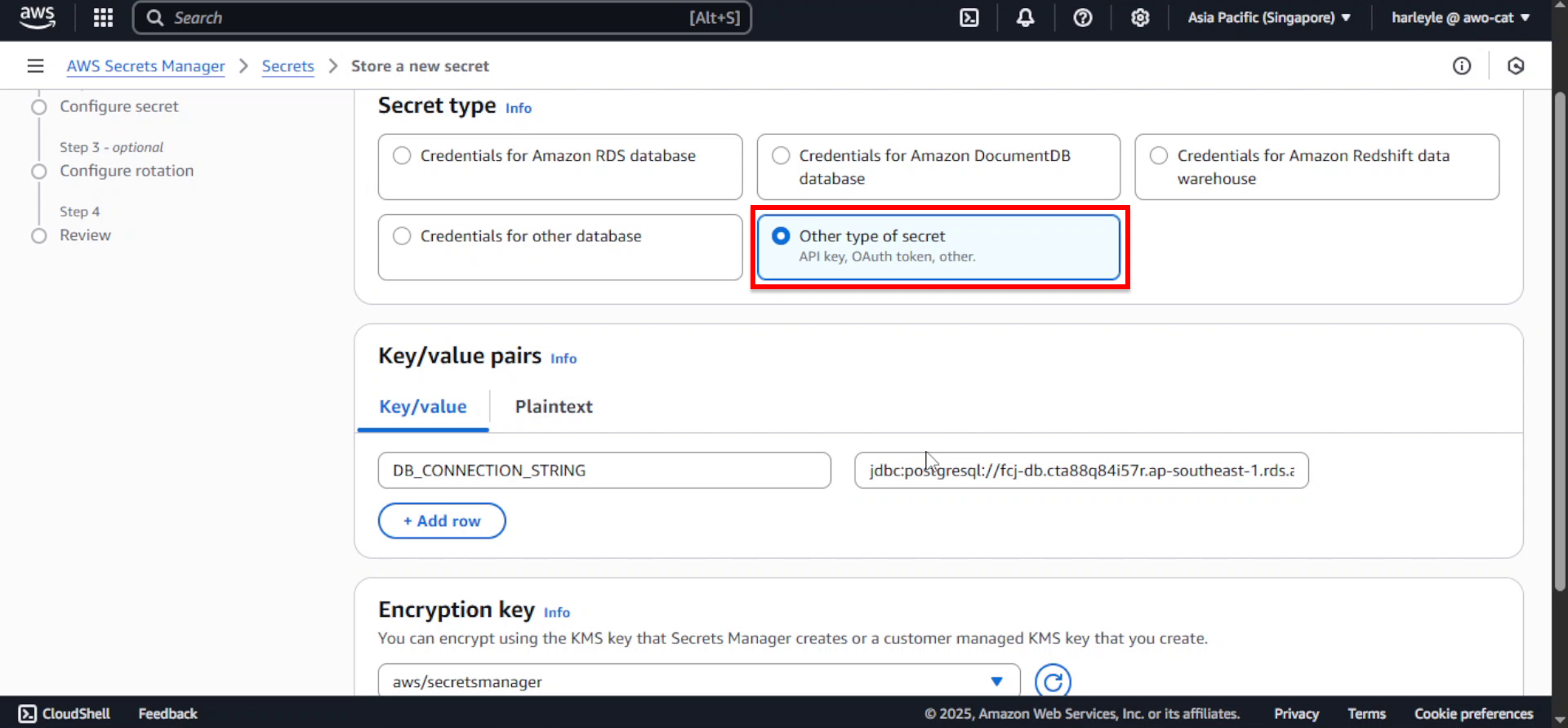
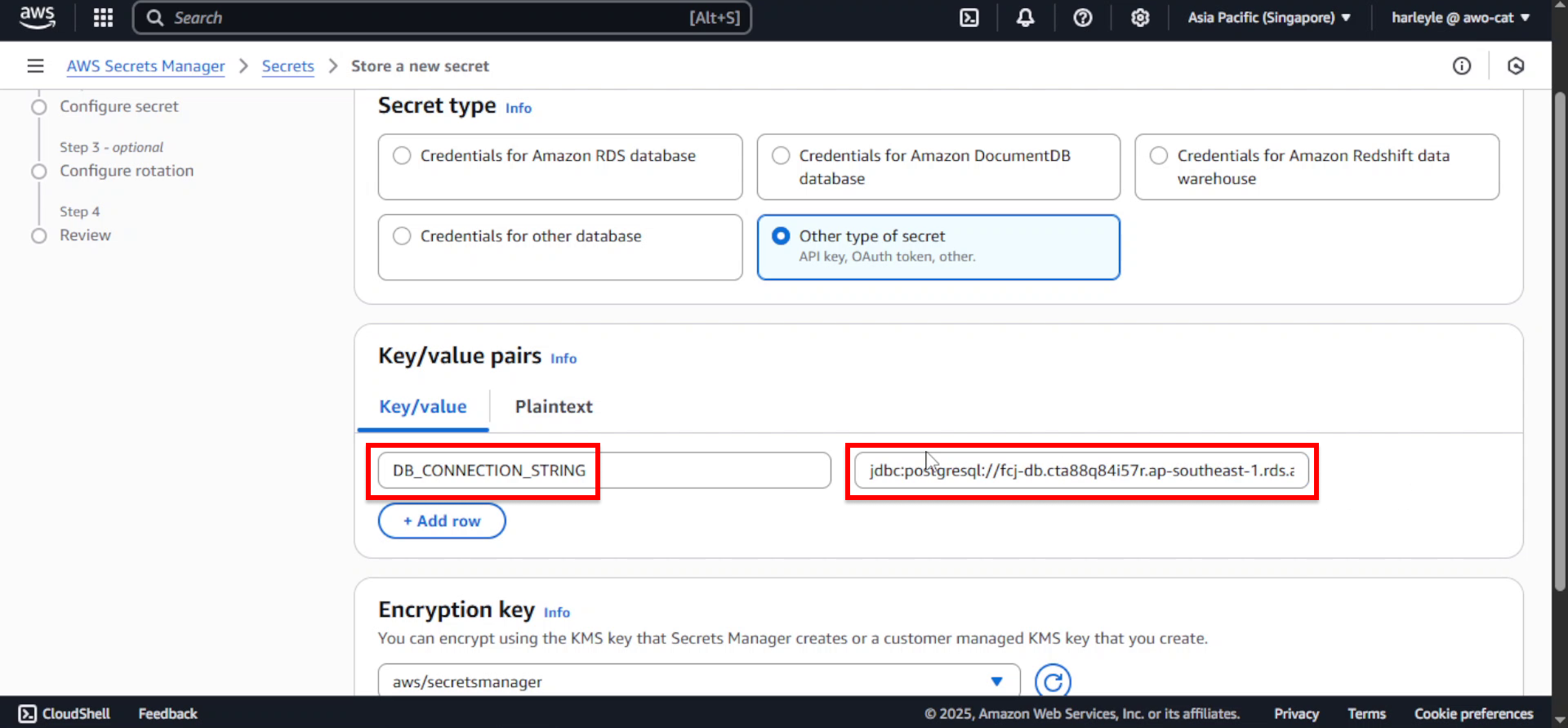
6. Configure the key-value pair:
- Key: Enter
DB_CONNECTION_STRING - Value: Enter
jdbc:postgresql://<DATABASE_ENDPOINT>:5432/FCJMomentum?user=postgres&password=fcj-db-123 - Replace
<DATABASE_ENDPOINT>with your actual database endpoint from step 2
7. Click Next.
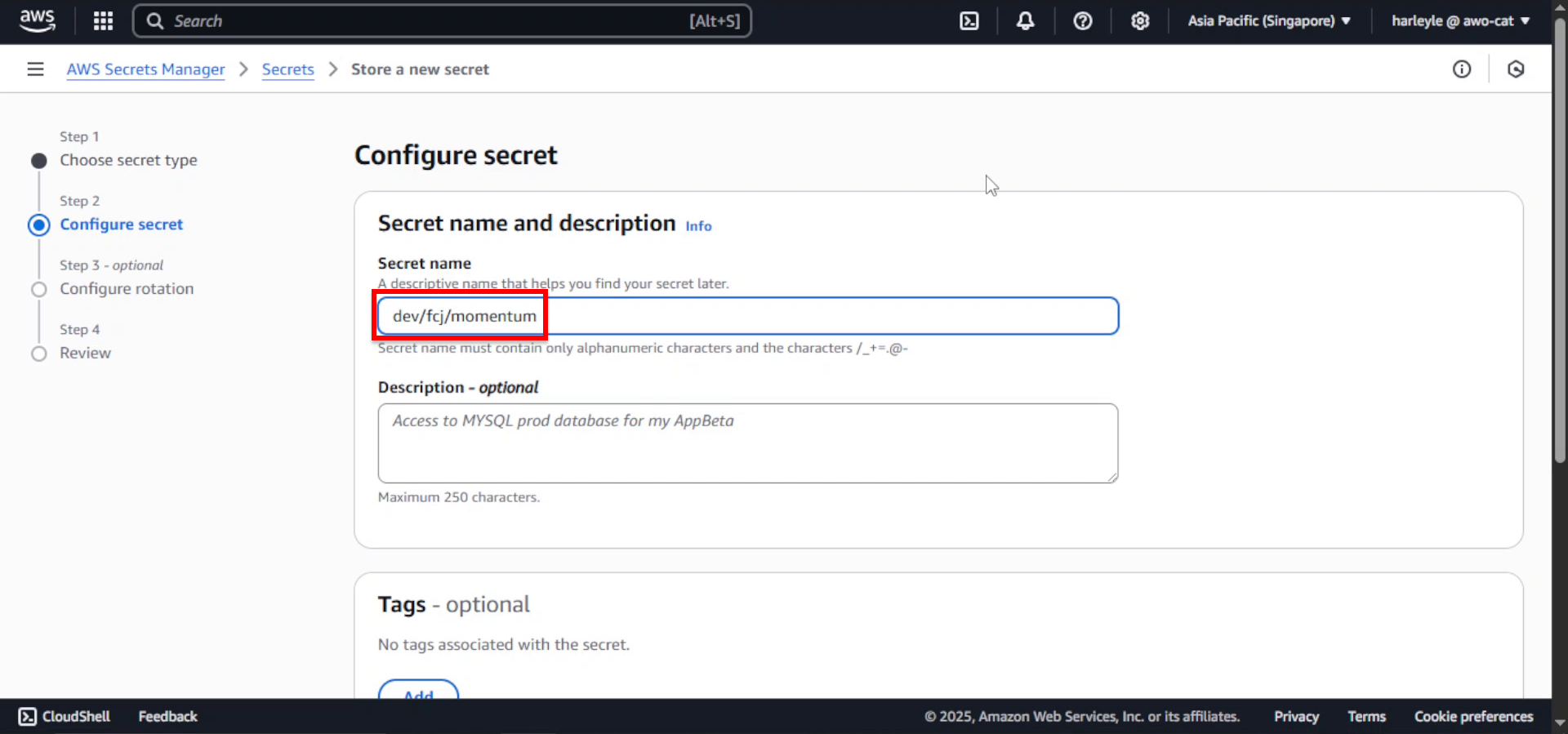
8. Configure the secret name:
- Secret name: Enter
dev/fcj/momentum - Description: (Optional) Enter
Database connection string for FCJ Momentum application
9. Scroll down and click Next.
10. Configure rotation (optional):
- Keep the default settings (no automatic rotation)
- Click Next
11. Review and create:
- Review your configuration
- Verify the connection string is correct
- Click Store
12. Verify creation: Confirm that the secret dev/fcj/momentum appears in your Secrets Manager console with the correct key-value pair.
Your database connection string is now securely stored in AWS Secrets Manager and ready to be used by your ECS tasks and CodeBuild projects.
